What Causes Forest Fires

One of the primary causes of forest fires is lightning. When lightning strikes dry vegetation, it can ignite a fire that quickly spreads through the forest. Even a single bolt of lightning can trigger a devastating blaze, especially during periods of drought when the vegetation is particularly dry and flammable. Additionally, human activities such as campfires left unattended, discarded cigarettes, and equipment malfunctions can also spark forest fires. With more people living and recreating in wildland areas, the risk of accidental fires caused by human actions has increased significantly.
• Lightning strikes dry vegetation, igniting fires that spread quickly
• Single bolt of lightning can trigger devastating blaze, especially during drought
• Human activities like unattended campfires, discarded cigarettes, and equipment malfunctions also cause forest fires
• Increased risk of accidental fires due to more people living and recreating in wildland areas
The Role of Climate and Weather
Climate and weather play a crucial role in influencing the behavior and spread of forest fires. Hot and dry conditions make forests more susceptible to ignition and rapid fire spread. Low humidity levels can also contribute to the drying out of vegetation, increasing the potential for fires to start and escalate quickly. Additionally, strong winds can fan the flames, causing fires to spread more rapidly and become more difficult to control.
Moreover, prolonged periods of drought can create conditions that are ripe for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly. Lack of moisture in the soil and vegetation during droughts makes forests more vulnerable to ignition from various sources such as lightning strikes or human activities. These dry conditions can also result in larger and more intense fires that are challenging for firefighters to contain and extinguish.
• Hot and dry conditions make forests more susceptible to ignition
• Low humidity levels can contribute to drying out vegetation
• Strong winds can fan the flames and cause fires to spread rapidly
• Prolonged droughts create conditions ripe for wildfires to ignite and spread quickly
• Lack of moisture in soil and vegetation during droughts makes forests vulnerable to ignition from various sources
Human Activities that Increase Fire Risk
Humans play a significant role in increasing the risk of forest fires through various activities. One of the primary contributors to the ignition of wildfires is the careless disposal of smoking materials, such as cigarettes, which can easily ignite dry vegetation. Additionally, the use of machinery and equipment in hot and dry conditions, like chainsaws and lawnmowers, without proper precautions can spark fires.
Another common human activity that escalates the danger of wildfires is the burning of debris or yard waste without following proper guidelines and regulations. Uncontrolled burns can quickly get out of hand and spread to surrounding vegetation, leading to destructive wildfires. Furthermore, the irresponsible use of campfires, fireworks, and other open flames in fire-prone areas can also result in the accidental ignition of fires that can quickly escalate and threaten communities and ecosystems.
• Careless disposal of smoking materials, such as cigarettes
• Use of machinery and equipment in hot and dry conditions without precautions
• Burning of debris or yard waste without following proper guidelines
• Irresponsible use of campfires, fireworks, and open flames in fire-prone areas
The Impact of Drought on Fire Behavior
Drought exerts a significant influence on fire behavior, creating ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly through dry vegetation. When moisture levels in the environment diminish due to prolonged drought, vegetation becomes highly flammable, intensifying the potential for fires to ignite and escalate. The lack of moisture in the soil and vegetation during drought periods increases the likelihood of fires starting and makes them more difficult to control once ignited.
Furthermore, drought conditions can lead to an overall increase in the frequency and severity of wildfires. As dry conditions persist, the landscape becomes more susceptible to fires, with the potential for larger and more destructive fire events. The combination of dry vegetation, low humidity, and high temperatures during drought periods creates a dangerous environment where fires can quickly grow out of control, posing a significant threat to both the environment and human communities.
• Drought creates ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly
• Lack of moisture in soil and vegetation increases likelihood of fires starting
• Dry vegetation, low humidity, and high temperatures during drought periods create dangerous environment for fires to grow out of control
• Drought can lead to an overall increase in frequency and severity of wildfires
The Role of Wind in Spreading Fires
In the spread of forest fires, wind plays a crucial role in accelerating the rate at which fires advance through landscapes. When strong winds are present, they can push flames in multiple directions, carrying embers ahead of the main fire front and causing new spot fires to ignite. Additionally, wind can influence the intensity of a fire by increasing oxygen supply and drying out vegetation, making it more susceptible to ignition.
Fire behavior analysts carefully monitor wind patterns during wildfire incidents to predict how the fire will spread and where it might pose the greatest threat. With wind being a dynamic and sometimes unpredictable factor, firefighters must adapt their strategies based on changing wind speeds and directions to effectively contain and control the fire. By understanding the role of wind in spreading fires, fire management agencies can better allocate resources and coordinate efforts to mitigate the impact of wildfires on ecosystems and communities.
• Wind accelerates the rate at which fires advance through landscapes
• Strong winds can push flames in multiple directions, carrying embers ahead of the main fire front
• Wind influences the intensity of a fire by increasing oxygen supply and drying out vegetation
• Fire behavior analysts monitor wind patterns to predict fire spread and potential threats
• Firefighters must adapt strategies based on changing wind speeds and directions to contain fires effectively
• Understanding the role of wind helps in better resource allocation and coordination for wildfire mitigation efforts
How Topography Affects Fire Spread
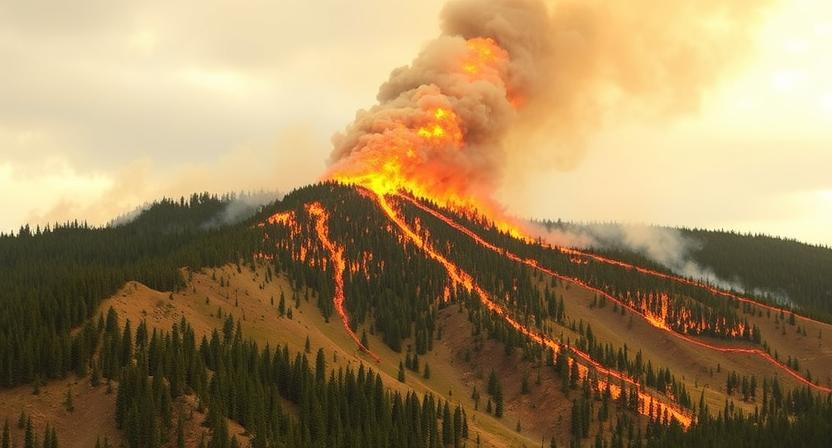

Topography plays a crucial role in influencing the behavior and spread of forest fires. In hilly or mountainous terrain, fires move more quickly uphill due to the preheating of fuel and increased wind speed. As the flames move uphill, they can leap from treetop to treetop, creating a phenomenon known as crowning that allows fires to spread rapidly and unpredictably.
Conversely, fires tend to move more slowly downhill as the heat and flames are reduced due to the lack of preheated fuel. However, fires can still pose a threat downhill as burning debris and embers can roll downhill ahead of the main fire, potentially igniting new areas and spreading the fire in multiple directions. Topographical features such as valleys can also influence fire behavior by funneling and intensifying winds, which can quickly spread the fire across the landscape.
• In hilly or mountainous terrain, fires move more quickly uphill
• Preheating of fuel and increased wind speed contribute to faster fire spread
• Crowning phenomenon allows fires to spread rapidly and unpredictably when flames leap from treetop to treetop
• Fires tend to move more slowly downhill due to reduced heat and flames
• Burning debris and embers can roll downhill ahead of the main fire, igniting new areas
• Valleys can funnel and intensify winds, spreading the fire quickly across the landscape
The Importance of Fuel Types in Fire Behavior
Different types of fuels in a forest play a crucial role in determining the behavior of a fire. Fine fuels such as dry grass and leaves ignite easily and can quickly spread a fire. These fuels contribute to the intensity of a fire, making it more difficult to control and extinguish.
In contrast, larger fuels such as fallen trees and logs burn slower and at higher temperatures. These fuels can create long-lasting hot spots within a fire, posing challenges to firefighters as they work to contain the blaze. Understanding the different fuel types present in a forest is essential for developing effective fire management strategies and preemptive measures to prevent catastrophic wildfires.
• Fine fuels like dry grass and leaves ignite easily and spread quickly
• Fine fuels contribute to the intensity of a fire, making it harder to control
• Larger fuels such as fallen trees burn slower and at higher temperatures
• Larger fuels create long-lasting hot spots within a fire, posing challenges for firefighters
• Understanding different fuel types is crucial for developing effective fire management strategies
The Role of Firefighters in Controlling Fires
Firefighters play a crucial role in controlling and extinguishing forest fires. Their bravery and expertise are vital in combating the unpredictable and dangerous nature of wildfires. When faced with a blaze, firefighters work tirelessly to contain the fire, protect communities, and prevent further destruction of valuable natural resources.
Firefighters utilize specialized equipment and training to battle wildfires on the front lines. Their efforts involve constructing fire lines, conducting backburns, and strategically deploying resources to suppress the spread of flames. Additionally, firefighters work collaboratively with other emergency responders and agencies to coordinate efforts and efficiently manage fire incidents. Their dedication and quick response are essential in mitigating the impact of wildfires and safeguarding both lives and property.
• Firefighters play a crucial role in controlling and extinguishing forest fires
• Their bravery and expertise are vital in combating the unpredictable and dangerous nature of wildfires
• When faced with a blaze, firefighters work tirelessly to contain the fire, protect communities, and prevent further destruction of valuable natural resources
Firefighters utilize specialized equipment and training to battle wildfires on the front lines.
Their efforts involve:
• Constructing fire lines
• Conducting backburns
• Strategically deploying resources to suppress the spread of flames
Additionally, firefighters work collaboratively with other emergency responders and agencies to coordinate efforts and efficiently manage fire incidents.
Their dedication and quick response are essential in mitigating the impact of wildfires and safeguarding both lives and property.
Tools and Techniques Used to Fight Forest Fires
When it comes to fighting forest fires, firefighters employ a variety of tools and techniques to contain and extinguish the flames. One of the primary tools used is the fire hose, which allows firefighters to deliver water or fire retardant to the fire line. These hoses are essential in controlling the spread of the fire and protecting surrounding areas from further damage. In addition to hoses, firefighters also use hand tools such as shovels, axes, and chainsaws to create firebreaks and remove vegetation to prevent the fire from spreading.
Another key technique used in fighting forest fires is the creation of containment lines. Firefighters strategically clear areas of vegetation to create firebreaks that can help stop the spread of the fire. These containment lines act as barriers to contain the fire within a specific area, allowing firefighters to focus their efforts on extinguishing the flames. Additionally, firefighters may use backburning techniques, where small controlled fires are set ahead of the main fire to consume fuel sources and create a buffer zone, reducing the intensity of the main fire.
• Fire hose is a primary tool used by firefighters to deliver water or fire retardant
• Hand tools such as shovels, axes, and chainsaws are used to create firebreaks
• Containment lines are strategically created by clearing vegetation to stop the spread of fire
• Backburning techniques involve setting small controlled fires ahead of the main fire
The Use of Firebreaks to Control Fire Spread
Firebreaks are a crucial tool in controlling the spread of wildfires. These strategically placed barriers act as a buffer by creating gaps devoid of vegetation or fuel, hindering the progress of the fire. By impeding the fire’s advance, firefighters gain the upper hand in containing and extinguishing the blaze before it engulfs more land.
The effectiveness of firebreaks lies in their ability to break the continuity of vegetation, essentially creating a barrier that hampers the fire’s ability to jump and spread rapidly. This proactive approach to fire management not only protects lives and property but also plays a vital role in safeguarding the natural ecosystem from the devastating impact of uncontrolled wildfires.
• Firebreaks create gaps devoid of vegetation or fuel
• Hinders the progress of the fire
• Gives firefighters an advantage in containing and extinguishing the blaze
The strategic placement of firebreaks is essential in maximizing their effectiveness. They are often strategically positioned along natural barriers such as rivers, roads, or rocky terrain to enhance their ability to halt the spread of wildfires. Additionally, regular maintenance and clearing of these firebreaks are necessary to ensure they remain effective in preventing fires from spreading uncontrollably.
• Strategically placed along natural barriers
• Regular maintenance and clearing required for effectiveness
In addition to physical firebreaks, prescribed burns can also be used as a preventive measure to reduce fuel loads and minimize the risk of large-scale wildfires. By intentionally setting controlled fires under specific conditions, land managers can decrease excess vegetation that could potentially fuel a wildfire. This proactive approach helps mitigate the intensity and size of future fires while promoting overall ecosystem health.
• Prescribed burns help reduce fuel loads
• Mitigates intensity and size of future fires
• Promotes overall ecosystem health
The Role of Aerial Firefighting in Containment Efforts
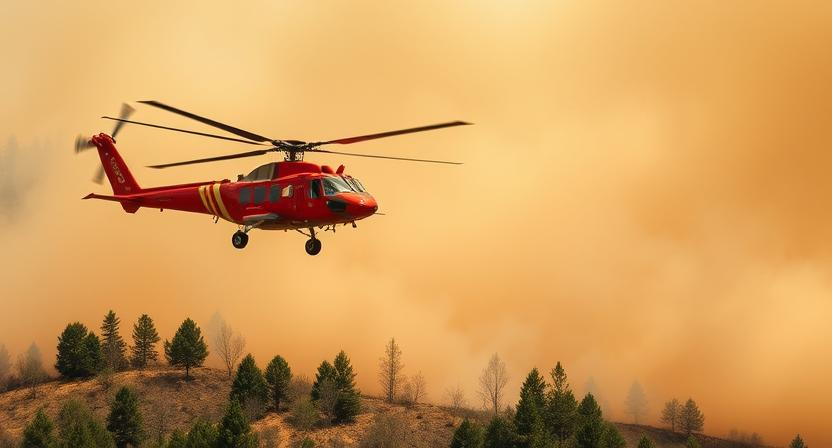

Aerial firefighting plays a crucial role in the containment efforts of wildfires, particularly in hard-to-reach areas where ground crews might face challenges in accessing the flames. Helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft are deployed to drop water, fire retardants, or foam directly onto the burning areas. This swift and strategic aerial support helps to slow down the fire’s progression and create fire lines to prevent further spread into vulnerable regions.
The use of aerial firefighting also aids in protecting valuable natural resources, infrastructure, and human lives. By targeting specific hotspots and providing a bird’s eye view of the fire’s behavior, aerial crews assist ground teams in coordinating their efforts effectively. Additionally, these aircraft can work in conjunction with ground crews to create a multi-pronged approach to fire suppression, enhancing the overall containment strategy and increasing the chances of successfully controlling the wildfire.
• Aerial firefighting is essential in reaching hard-to-access areas where ground crews may struggle
• Helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft drop water, fire retardants, or foam directly onto burning areas
• Swift aerial support helps slow down fire progression and create fire lines to prevent further spread
• Protects natural resources, infrastructure, and human lives by targeting specific hotspots
• Provides a bird’s eye view of the fire’s behavior to assist ground teams in coordinating efforts efficiently
• Works with ground crews to create a multi-pronged approach to fire suppression
The Importance of Early Detection and Reporting
Early detection and reporting of forest fires play a crucial role in preventing small incidents from escalating into unmanageable infernos. With the help of vigilant individuals, advanced technology, and dedicated surveillance systems, spotting a fire in its initial stages becomes achievable. Timely reporting ensures that firefighting resources can be deployed swiftly to contain the blaze before it spreads further.
Furthermore, early detection and reporting not only save lives and protect property but also safeguard the ecosystem and wildlife habitats from the devastating impacts of unrestrained wildfires. By remaining alert and promptly notifying authorities about suspected fires, communities can contribute significantly to mitigating the destructive consequences of such natural disasters. This proactive approach underscores the importance of fostering a cooperative and responsive attitude towards fire prevention and control efforts.
• Early detection and reporting are essential in preventing forest fires from escalating
• Vigilant individuals, advanced technology, and surveillance systems help in spotting fires early
• Timely reporting allows for swift deployment of firefighting resources to contain the blaze
Early detection and reporting not only save lives and protect property but also safeguard the ecosystem and wildlife habitats. By staying alert and notifying authorities promptly about suspected fires, communities can play a crucial role in mitigating the destructive impacts of wildfires. This proactive approach emphasizes the significance of fostering a cooperative and responsive attitude towards fire prevention efforts.
The Role of Fire Weather Forecasting in Fire Management
Fire weather forecasting plays a crucial role in the effective management of wildfires. By accurately predicting weather conditions such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed, forecasters can provide vital information to fire management agencies to help them anticipate fire behavior and spread. This forecasting allows firefighting teams to plan their strategies and allocate resources more effectively, ultimately increasing their chances of successfully containing and controlling wildfires.
Additionally, fire weather forecasting helps in issuing timely warnings and advisories to residents in fire-prone areas, enabling them to take necessary precautions and evacuate if required. By monitoring changing weather patterns and providing real-time updates on fire weather conditions, forecasters play a key role in enhancing overall public safety and reducing the risk of wildfires becoming uncontrollable. Overall, accurate fire weather forecasting is an essential tool in the proactive approach to wildfire management and prevention.
• Fire weather forecasting provides vital information to fire management agencies
• Helps firefighting teams plan strategies and allocate resources effectively
• Increases chances of successfully containing and controlling wildfires
• Enables timely warnings and advisories to residents in fire-prone areas
• Allows residents to take necessary precautions and evacuate if required
• Enhances overall public safety and reduces the risk of uncontrollable wildfires
Accurate fire weather forecasting is an essential tool in the proactive approach to wildfire management and prevention. By predicting weather conditions accurately, forecasters play a crucial role in helping firefighting teams anticipate fire behavior, plan strategies, allocate resources effectively, issue timely warnings to residents, and ultimately increase public safety. The role of fire weather forecasting cannot be overstated when it comes to managing wildfires efficiently.
Community Preparedness and Evacuation Plans
Community preparedness plays a crucial role in ensuring safety during wildfire outbreaks. Communities need to establish clear evacuation plans that outline designated escape routes, meeting points, and communication channels. Regular drills and exercises should be conducted to familiarize residents with these plans and ensure a swift response in times of emergency.
Additionally, community members should be educated on the importance of being proactive and vigilant in fire-prone areas. This includes maintaining defensible space around homes, having emergency kits ready, and staying informed about fire weather conditions. Collaboration among residents, local authorities, and emergency response teams is essential for effective evacuation procedures and minimizing the potential impact of wildfires on communities.
• Establish clear evacuation plans with designated escape routes, meeting points, and communication channels
• Conduct regular drills and exercises to familiarize residents with evacuation plans
• Educate community members on being proactive and vigilant in fire-prone areas
• Maintain defensible space around homes
• Have emergency kits ready for quick evacuation
• Stay informed about fire weather conditions
• Collaborate with residents, local authorities, and emergency response teams for effective evacuation procedures
The Importance of Prescribed Burns in Fire Prevention
Prescribed burns play a crucial role in fire prevention by reducing the build-up of flammable vegetation in forests. By intentionally setting controlled fires under specific conditions, land managers can help mimic natural fire cycles and create fire-resistant landscapes. These controlled burns help prevent larger, more destructive wildfires by reducing the amount of fuel available to burn.
In addition to reducing fuel loads, prescribed burns also promote forest health by rejuvenating ecosystems and promoting the growth of native vegetation. By eliminating invasive species and promoting the growth of fire-resistant plant communities, prescribed burns help create a more resilient landscape that is better equipped to withstand and recover from wildfires. Overall, prescribed burns are an important tool in the toolbox of fire managers to help prevent and mitigate the impact of wildfires on forests and surrounding communities.
• Prescribed burns reduce build-up of flammable vegetation
• Mimic natural fire cycles and create fire-resistant landscapes
• Prevent larger, more destructive wildfires by reducing fuel available to burn
• Promote forest health by rejuvenating ecosystems and promoting growth of native vegetation
• Eliminate invasive species and promote growth of fire-resistant plant communities
• Create a more resilient landscape better equipped to withstand and recover from wildfires
The Impact of Climate Change on Forest Fires

Climate change is having a profound impact on the frequency and intensity of forest fires around the world. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and changing precipitation patterns are creating conditions that are conducive to larger and more destructive fires. These changes not only increase the likelihood of fires starting, but also make them harder to contain and extinguish, posing significant challenges to fire management agencies.
In addition to altering the environmental conditions that fuel fires, climate change is also affecting the length of fire seasons. With warmer temperatures and drier conditions persisting for longer periods of time, the window for potential fire activity is widening, increasing the overall risk of devastating wildfires. This prolonged fire season puts additional strain on firefighting resources and increases the potential for fires to spread and cause widespread damage to both ecosystems and communities.
• Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and changing precipitation patterns are creating conditions conducive to larger and more destructive fires.
• Changes make fires harder to contain and extinguish, posing challenges to fire management agencies.
• Climate change is affecting the length of fire seasons with warmer temperatures and drier conditions persisting for longer periods of time.
• Widening window for potential fire activity increases overall risk of devastating wildfires.
• Prolonged fire season puts strain on firefighting resources and increases potential for fires to spread and cause widespread damage.
The Role of Fire Management Agencies in Fire Control
Fire management agencies play a crucial role in controlling and preventing wildfires. These agencies are responsible for coordinating firefighting efforts, implementing fire prevention strategies, and managing resources to effectively combat wildfires. They work closely with local, state, and federal agencies, as well as other stakeholders, to ensure a coordinated and efficient response to fire incidents.
Through their expertise, resources, and collaboration with other organizations, fire management agencies are able to deploy firefighting teams, utilize specialized equipment, and implement strategic plans to contain and extinguish wildfires. Their proactive approach to fire control, including monitoring fire weather conditions, enhancing public awareness, and implementing prescribed burn programs, helps to mitigate the impact of wildfires on communities and natural habitats.
• Fire management agencies are responsible for coordinating firefighting efforts
• They implement fire prevention strategies to reduce the risk of wildfires
• These agencies manage resources effectively to combat wildfires
• Collaboration with local, state, and federal agencies ensures a coordinated response
• Expertise and resources allow for deployment of firefighting teams and specialized equipment
• Proactive measures such as monitoring fire weather conditions help mitigate wildfire impact on communities
International Cooperation in Firefighting Efforts
International cooperation plays a crucial role in firefighting efforts, particularly in managing large-scale forest fires that may cross international borders. When facing such challenges, countries must work together to share resources, expertise, and best practices to effectively combat these fires. By collaborating on a global scale, firefighting teams can benefit from each other’s strengths and experiences, leading to more efficient and coordinated fire control operations.
Additionally, international cooperation fosters mutual support and solidarity among nations during times of crisis. By coming together to combat forest fires, countries demonstrate unity and a shared commitment to protecting their natural landscapes and communities. This collaborative approach not only enhances firefighting capabilities but also strengthens relationships between nations, promoting a sense of solidarity and global responsibility in addressing the common threat of wildfires.
• International cooperation is essential for managing large-scale forest fires that may cross borders
• Countries must work together to share resources, expertise, and best practices
• Collaboration on a global scale leads to more efficient and coordinated fire control operations
• Mutual support and solidarity among nations are fostered during times of crisis through international cooperation
• Collaborative efforts demonstrate unity and shared commitment to protecting natural landscapes and communities
• Strengthening relationships between nations promotes a sense of solidarity and global responsibility in addressing wildfires
The Importance of Public Education and Awareness
Public education and awareness play a crucial role in preventing and mitigating the impact of forest fires. By educating individuals about the causes of wildfires and the steps they can take to reduce fire risks, communities can work together to create a safer environment. Increasing awareness about the importance of fire safety practices such as proper disposal of cigarettes, campfire regulations, and the use of equipment with sparks can significantly decrease the likelihood of unintentional fires.
Moreover, public education efforts can also focus on promoting early detection and reporting of wildfires. By educating individuals on how to recognize the signs of a potential fire and the importance of reporting it promptly to fire authorities, communities can help expedite response times and prevent small fires from escalating into larger, more destructive ones. Additionally, raising awareness about the significance of adhering to fire bans and restrictions during periods of high fire danger can further aid in minimizing the occurrence of wildfires.
– Proper disposal of cigarettes
– Campfire regulations
– Use of equipment with sparks
– Recognizing signs of potential fires
– Prompt reporting to fire authorities
– Adhering to fire bans and restrictions during high fire danger periods
The Future of Fire Management and Prevention.
As we look ahead to the future of fire management and prevention, advancements in technology will play a crucial role in enhancing our capabilities to combat wildfires. From the development of more sophisticated fire detection systems using drones and satellite imagery to the utilization of artificial intelligence for fire behavior prediction, the integration of technology will revolutionize how we approach wildfire management.
Furthermore, increased collaboration and coordination among local, national, and international firefighting agencies will be essential in tackling the growing threat of wildfires. By sharing resources, expertise, and best practices, we can improve our response to wildfires and effectively protect communities and the environment. Emphasizing proactive measures such as prescribed burns and community preparedness will also be key in mitigating the impact of wildfires in the future.
• Enhanced fire detection systems using drones and satellite imagery
• Utilization of artificial intelligence for fire behavior prediction
• Increased collaboration among local, national, and international firefighting agencies
• Sharing resources, expertise, and best practices to improve response to wildfires
• Emphasizing proactive measures such as prescribed burns and community preparedness