Factors influencing wildlife migration patterns
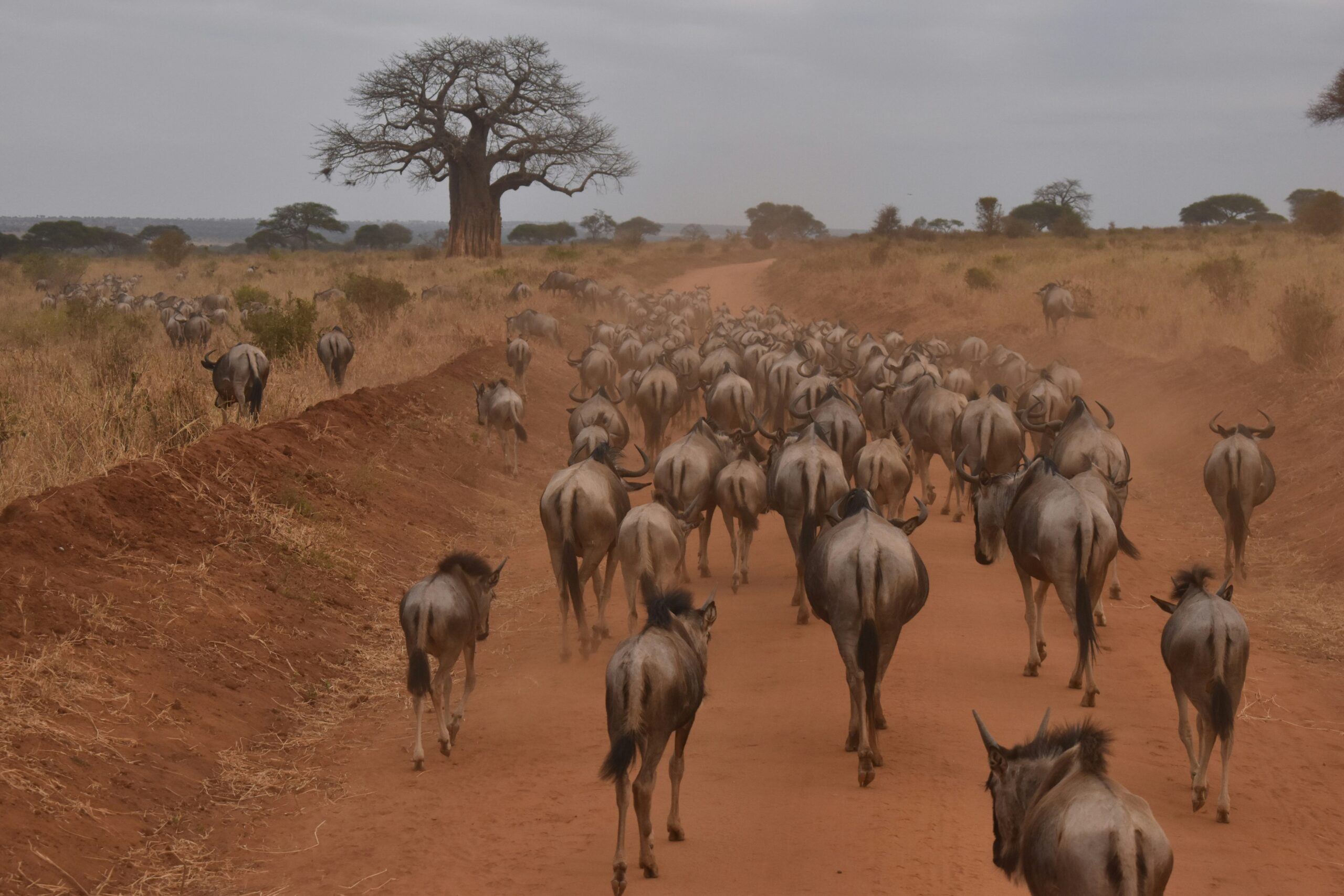
Wildlife migration patterns are complex phenomena shaped by a multitude of factors. From the availability of food sources to the presence of predators, various elements come into play when animals embark on their seasonal journeys. The topography of the landscape also plays a crucial role in guiding migrations, influencing the routes that animals take to reach their desired destinations.
Climate is another key factor that significantly impacts wildlife migration patterns. Changes in temperature and precipitation can alter migration routes, affecting the timing and duration of journeys. Additionally, natural disasters such as wildfires, droughts, and floods can force animals to adapt their movements to ensure their survival. Understanding these diverse factors is essential in comprehending the intricate nature of wildlife migration and the challenges animals face in their quest for survival.
• Availability of food sources
• Presence of predators
• Topography of the landscape
• Climate changes (temperature, precipitation)
• Natural disasters (wildfires, droughts, floods)
Impact of climate on migration routes
Climate plays a crucial role in shaping wildlife migration routes. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can directly influence the availability of food and water sources along the way. Furthermore, alterations in climate can impact vegetation growth, affecting the suitability of habitats for resting and breeding during migration.
In addition to affecting resource availability, climate also influences the timing and duration of migration for many species. Warmer temperatures may lead to shifts in migration schedules, altering the presence of certain species in specific locations at different times of the year. Extreme weather events linked to climate change, such as severe storms or prolonged droughts, can disrupt traditional migration patterns and force wildlife to adapt their routes in response to these environmental challenges.
• Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can directly influence the availability of food and water sources along migration routes.
• Alterations in climate can impact vegetation growth, affecting the suitability of habitats for resting and breeding during migration.
• Warmer temperatures may lead to shifts in migration schedules, altering the presence of certain species in specific locations at different times of the year.
• Extreme weather events linked to climate change, such as severe storms or prolonged droughts, can disrupt traditional migration patterns.
Role of topography in guiding migrations
Topography plays a crucial role in shaping wildlife migration patterns. The physical features of the landscape, such as mountains, rivers, and valleys, act as natural guides for the movement of animals. These geographical characteristics can either facilitate or hinder the progress of migrating species, influencing the routes they take to reach their destination.
Mountains, for instance, can present significant obstacles for animals migrating across vast distances. The steep slopes and rugged terrain may force wildlife to find alternative pathways, leading to longer migration routes or even detours. On the other hand, valleys and plains can provide smoother pathways for animals to navigate, allowing for more efficient and direct migrations. Topography acts as a navigational aid for wildlife, shaping their movements and defining the paths they follow during their seasonal journeys.
• Mountains can present obstacles for migrating animals
• Steep slopes and rugged terrain may force wildlife to find alternative pathways
• Valleys and plains provide smoother pathways for migration
• Topography acts as a navigational aid for wildlife during seasonal journeys
Influence of food availability on wildlife movements
Providing a driving force for wildlife movements, the availability of food plays a crucial role in dictating the patterns and extent of animal migrations. As various species rely on specific types of resources to sustain themselves, the quest for nourishment often propels them towards areas where these essentials are abundant. Whether it be lush grazing pastures for herbivores or regions abundant in prey for carnivorous creatures, the pursuit of sustenance acts as a compelling force shaping the movements of wildlife across vast landscapes.
Furthermore, fluctuations in food availability can trigger long journeys as animals seek out alternative sources to meet their nutritional needs. In times of scarcity, species may be required to travel greater distances in search of suitable feeding grounds, sometimes even leading to unfamiliar territories. Consequently, the ebb and flow of food resources not only influence the day-to-day movements of wildlife but also have a profound impact on the seasonal and migratory behaviors exhibited by different species.
• The availability of food drives wildlife movements
• Different species rely on specific types of resources for sustenance
• Scarcity of food can lead to animals traveling greater distances in search of suitable feeding grounds
• Fluctuations in food availability influence both daily and seasonal movements of wildlife
Effect of water sources on migration behavior
Water sources play a crucial role in shaping the migration behavior of wildlife species. Animals often rely on these sources for hydration, nourishment, and even as landmarks along their migratory routes. The availability of water can act as a magnet, drawing animals towards these essential resources during their journeys.
During migrations, water sources also serve as rest stops for tired and weary travelers. Animals may congregate near these sources to replenish their energy reserves before continuing their arduous journeys. The presence or absence of water along migration routes can greatly influence the success of these movements, with animals strategically planning their movements around these vital resources.
• Water sources act as magnets for wildlife during migrations
• Animals rely on water for hydration, nourishment, and as landmarks along their routes
• Availability of water can greatly influence the success of migration movements
• Water sources serve as rest stops for tired travelers during migrations
• Animals strategically plan their movements around vital water resources
Relationship between geography and breeding grounds
Breeding grounds are essential habitats where wildlife species carry out key reproductive activities to ensure the survival of their populations. These areas are intricately linked to the geography of the surrounding landscape, as they provide the necessary resources and conditions for successful breeding. The geographical features of a region, such as the availability of suitable nesting sites, food sources, and shelter, play a critical role in determining the suitability of an area as a breeding ground for different species.
The relationship between geography and breeding grounds highlights how environmental factors shape the distribution and abundance of wildlife populations. For example, certain bird species may prefer breeding in specific types of forests with tall trees for nesting, while marine mammals may rely on coastal areas with access to rich feeding grounds for raising their young. By understanding how geography influences the locations of breeding grounds, conservation efforts can be targeted towards preserving these crucial habitats to support healthy populations of wildlife species.
• Breeding grounds are essential habitats for wildlife species to carry out key reproductive activities
• Geography of the surrounding landscape provides necessary resources and conditions for successful breeding
• Availability of suitable nesting sites, food sources, and shelter play a critical role in determining suitability of an area as a breeding ground
• Environmental factors shape distribution and abundance of wildlife populations
• Certain bird species may prefer breeding in specific types of forests with tall trees for nesting
• Marine mammals may rely on coastal areas with access to rich feeding grounds for raising their young
• Understanding how geography influences locations of breeding grounds can help target conservation efforts towards preserving crucial habitats
Significance of habitat fragmentation in migration patterns
The fragmentation of habitats due to human activities such as urbanization, deforestation, and agriculture has a substantial impact on wildlife migration patterns. As natural landscapes are divided and disrupted, animals face barriers that impede their traditional movement routes. This can lead to isolated populations, reduced genetic diversity, and challenges in finding suitable breeding grounds or necessary resources. Species that rely on extensive areas for feeding or breeding are particularly affected by habitat fragmentation, as it can limit their ability to access essential habitats.
Furthermore, habitat fragmentation can increase the vulnerability of wildlife to threats such as predation, competition for resources, and climate change. When migration routes are interrupted or altered, animals may be forced to navigate through unfamiliar or inhospitable environments, putting them at higher risk of predation or exhaustion. Additionally, fragmented habitats may not provide adequate shelter or food sources along the migration path, leading to decreased survival rates and reproductive success for many species.
• Habitat fragmentation due to human activities impacts wildlife migration patterns
• Animals face barriers that impede traditional movement routes
• Isolated populations, reduced genetic diversity, and challenges in finding suitable breeding grounds or resources can result
• Species relying on extensive areas for feeding or breeding are particularly affected
• Vulnerability to threats such as predation, competition for resources, and climate change increases with habitat fragmentation
• Altered migration routes can lead animals through unfamiliar or inhospitable environments
• Fragmented habitats may not provide adequate shelter or food sources along the migration path
Role of human activities in altering migration routes
Human activities have been known to significantly impact wildlife migration routes. The construction of roads, cities, and other infrastructure can create barriers that disrupt traditional migration paths. These physical obstructions can force animals to alter their routes or even prevent them from reaching important feeding or breeding grounds.
Furthermore, human development often leads to increased human-wildlife conflict, which can further influence migration patterns. As populations expand and encroach upon natural habitats, animals may be deterred from following their usual migration routes due to fear of human interference or danger. In some cases, this can result in wildlife populations becoming isolated or restricted to smaller areas, ultimately impacting their overall well-being and genetic diversity.
• Human activities such as construction of roads and cities can create barriers for wildlife migration
• Physical obstructions can force animals to alter their routes or prevent them from reaching important feeding or breeding grounds
• Increased human-wildlife conflict due to development can influence migration patterns
• Animals may be deterred from following usual routes due to fear of human interference or danger
• Wildlife populations becoming isolated or restricted to smaller areas can impact their well-being and genetic diversity
Effect of natural disasters on wildlife movements
Natural disasters can significantly impact wildlife movements by disrupting regular migration patterns. Events such as floods, wildfires, hurricanes, and earthquakes can force animals to alter their routes or even abandon traditional habitats. These sudden and often destructive occurrences can lead to confusion among wildlife populations, causing them to seek alternative paths or areas that may not be suitable for their needs.
The aftermath of a natural disaster can result in the loss of resources, destruction of habitats, and an increase in competition among species. This can further exacerbate the challenges faced by wildlife during migration, making it harder for them to find suitable shelter, food, and water. In some cases, these events can lead to shifts in population dynamics and an overall decline in certain wildlife species, highlighting the fragile balance that exists in the face of such environmental upheavals.
• Disruption of regular migration patterns
• Forced alteration of routes or abandonment of habitats
• Confusion among wildlife populations leading to seeking alternative paths
• Loss of resources and destruction of habitats post-disaster
• Increase in competition among species for survival
• Challenges in finding suitable shelter, food, and water during migration
• Shifts in population dynamics and decline in certain wildlife species
Influence of predators on migration behavior
Wildlife migrations are often influenced by the presence of predators along their routes. Predators play a crucial role in shaping the behavior of migrating animals, as the fear of being hunted can lead to strategic decision-making in terms of movement patterns and timing. For many species, the risk of encountering predators prompts them to choose specific migration routes that offer better cover or protection, allowing them to minimize the chances of being caught.
The pressure exerted by predators can also impact the speed and duration of migrations. Oftentimes, animals will accelerate their pace or prolong their journey to avoid areas with high predator activity. This adaptation showcases the intricate relationship between predators and the migration behavior of wildlife, highlighting the evolutionary importance of minimizing risk and maximizing survival chances during these critical journeys.
• Predators influence the migration behavior of wildlife by shaping movement patterns and timing
• Animals choose specific migration routes that offer better cover or protection to minimize the risk of being caught
• The pressure exerted by predators can impact the speed and duration of migrations
• Animals may accelerate their pace or prolong their journey to avoid areas with high predator activity
Impact of temperature on migration timing
Temperature plays a crucial role in determining the timing of wildlife migration. As temperatures shift throughout the year, animals often rely on these changes as signals to start or alter their migration patterns. For example, many bird species use temperature changes as cues to begin their long journeys to their breeding grounds. Warmer temperatures may trigger the start of migration as it signals the arrival of spring and the availability of resources needed for breeding and raising young.
Conversely, dropping temperatures in the fall serve as a prompt for many animals to start their migration towards warmer wintering grounds. This timing is essential for survival as it allows wildlife to escape harsh winter conditions and ensure access to food and shelter in more favorable habitats. The synchronization of migration with temperature changes demonstrates how closely wildlife are attuned to their environment and how crucial temperature cues are in guiding their movements throughout the year.
• Temperature plays a crucial role in determining the timing of wildlife migration
• Animals rely on temperature changes as signals to start or alter their migration patterns
• Many bird species use temperature changes as cues to begin their long journeys to breeding grounds
• Warmer temperatures may trigger the start of migration, signaling the arrival of spring and availability of resources needed for breeding and raising young
• Dropping temperatures in fall prompt many animals to start migrating towards warmer wintering grounds
• Timing of migration is essential for survival, allowing wildlife to escape harsh winter conditions and ensure access to food and shelter in more favorable habitats
Role of day length in triggering migrations
As days grow shorter or longer with the changing seasons, many species of wildlife are prompted to embark on their migratory journeys. The length of daylight serves as a critical environmental cue that triggers the movements of various animals across continents. This phenomenon is particularly evident in birds such as the Arctic Tern, known for its remarkable annual migration spanning from the Arctic to Antarctic regions based on the duration of daylight.
The intricate biological clock of migratory species is finely attuned to the variations in day length, signaling when it is time to begin their arduous journeys to more hospitable habitats. This natural phenomenon ensures that wildlife can capitalize on optimal conditions for breeding, foraging, or evading harsh weather by synchronizing their movements with the patterns of daylight. Ultimately, the role of day length in triggering migrations underscores the incredible adaptability and resilience of animals as they navigate vast distances in response to the subtle shifts in daylight duration.
• The length of daylight is a critical environmental cue for triggering migrations in many species
• Birds such as the Arctic Tern rely on day length to signal when it is time to begin their annual migration
• The biological clock of migratory species is finely attuned to variations in day length, allowing them to capitalize on optimal conditions for breeding and foraging
• Day length plays a key role in ensuring that wildlife can navigate vast distances and adapt to changing environmental conditions
Relationship between geography and seasonal changes
Geography plays a crucial role in dictating the seasonal changes that wildlife experience throughout the year. The varying landscapes, from mountains to deserts, forests to grasslands, influence the availability of resources such as food, shelter, and water for animals. These geographical features can drive migrations as animals move to follow the changing seasons and locate suitable habitats.
Understanding how geography affects seasonal changes is essential for wildlife conservation efforts. By mapping out the relationship between geography and seasonal variations, conservationists can identify crucial habitats and migration corridors that need protection. Preserving these areas is vital for ensuring the survival of various species in the face of environmental challenges such as climate change and habitat loss.
• Geography influences the availability of resources for animals
• Different landscapes drive migrations as animals seek suitable habitats
• Understanding this relationship is crucial for wildlife conservation efforts
• Mapping out geography and seasonal changes helps identify important habitats
• Protecting these areas is vital for species survival amidst environmental challenges
Significance of genetic factors in migration tendencies
Genetic factors play a crucial role in shaping the migration tendencies of wildlife populations. Through generations of adaptation and evolution, certain genetic characteristics have been selected for that drive animals to migrate in specific patterns. These genetic predispositions guide animals in seeking out favorable environments for breeding, feeding, and survival during different seasons.
Moreover, genetic factors also influence the timing and duration of migrations. Certain genes may trigger the initiation of migration in response to changing environmental cues such as temperature or day length. This genetic programming ensures that animals move at the most optimal times to maximize their chances of survival and reproductive success. Overall, the significance of genetic factors in migration tendencies highlights the intricate interplay between biological heritage and environmental influences in shaping wildlife movements.
• Genetic factors play a crucial role in shaping migration tendencies
• Through generations of adaptation and evolution, certain genetic characteristics drive animals to migrate in specific patterns
• Genetic predispositions guide animals in seeking out favorable environments for breeding, feeding, and survival during different seasons
• Genetic factors also influence the timing and duration of migrations
• Certain genes may trigger the initiation of migration in response to changing environmental cues such as temperature or day length
• Genetic programming ensures that animals move at the most optimal times to maximize their chances of survival and reproductive success
Effect of competition for resources on migration routes
Competition for resources plays a crucial role in shaping wildlife migration routes. As animals move across vast landscapes in search of food, water, and shelter, they often encounter competition from other species for these essential resources. This competition can influence the timing, speed, and direction of migrations, as animals adapt and adjust their routes to avoid conflicts and secure necessary provisions.
In times of scarcity, competition intensifies, leading to changes in migration patterns as animals seek out alternative resources. Some species may be forced to travel longer distances or navigate unfamiliar territories to find sustenance, impacting not only their own movements but also indirectly affecting the ecosystems they pass through. The struggle for resources can result in shifts in population dynamics, with dominant species outcompeting others and potentially altering the balance of wildlife communities along migration routes.
• Competition for resources shapes wildlife migration routes
• Animals encounter competition from other species for food, water, and shelter
• Timing, speed, and direction of migrations are influenced by competition
• In times of scarcity, competition intensifies leading to changes in migration patterns
As animals adapt and adjust their routes to avoid conflicts and secure necessary provisions. Some species may be forced to travel longer distances or navigate unfamiliar territories to find sustenance. This impacts not only their own movements but also indirectly affects the ecosystems they pass through. The struggle for resources can result in shifts in population dynamics, with dominant species outcompeting others and potentially altering the balance of wildlife communities along migration routes.
Role of instinct in guiding migration patterns
Instinct plays a crucial role in guiding wildlife migration patterns. It is an innate behavior that drives animals to move from one place to another in search of suitable habitats, food sources, or breeding grounds. This instinct is deeply rooted in the genetic makeup of species and has been honed through years of evolution to ensure the survival of individuals and populations.
Animals rely on this instinct to navigate long distances across varied landscapes and climates. Whether it is the migration of birds crossing continents or the movement of wildebeests across vast savannas, instinct serves as a compass guiding them on their journey. This intrinsic knowledge of when to migrate, where to go, and how to get there is a remarkable aspect of nature’s design that continues to fascinate researchers and conservationists alike.
• Instinct is an innate behavior that drives animals to move in search of suitable habitats
• It is deeply rooted in the genetic makeup of species and honed through evolution
• Animals rely on instinct to navigate long distances across varied landscapes and climates
• Migration patterns are guided by instinct, ensuring survival of individuals and populations
Influence of landscape features on migration speed
Wildlife migration speed is greatly influenced by the landscape features encountered along their journey. Open grasslands or flat terrains provide less resistance, allowing animals to move at a faster pace compared to traversing through dense forests or steep mountainous regions. For species like wildebeests or caribou that partake in long-distance migrations, the type of landscape they navigate can significantly impact the rate at which they travel.
Moreover, water bodies such as rivers and lakes can either impede or aid in migration speed depending on whether animals need to bypass or utilize them as a water source. Crossing large bodies of water may slow down migration progress, while access to smaller water sources can promote quicker movement. Landscape features like vegetation density, soil type, and elevation changes all play a crucial role in dictating how swiftly wildlife can migrate from one area to another.
• Open grasslands or flat terrains allow animals to move faster
• Dense forests or steep mountainous regions slow down migration speed
• Water bodies can impede or aid migration speed
o Large bodies of water may slow progress
o Smaller water sources can promote quicker movement
• Vegetation density, soil type, and elevation changes impact migration speed
Impact of urbanization on wildlife migration behavior
Urbanization exerts profound effects on wildlife migration behavior. The rapid expansion of urban areas often leads to habitat destruction and fragmentation, disrupting traditional migration routes and forcing animals to navigate unfamiliar and potentially perilous landscapes. As cities sprawl and infrastructure development accelerates, natural corridors that once facilitated smooth migration become obstructed or disappear entirely, posing significant challenges to the movement of many species.
Moreover, the presence of urban areas can introduce new threats to migrating wildlife. Increased vehicular traffic, pollution, noise, and artificial lights can all create barriers and hazards that alter animals’ behavior and impede their progress. For nocturnal species, artificial lighting can disrupt natural navigation cues, causing disorientation and potentially stranding animals in urban areas. These disruptions not only impact individual animals but can also have far-reaching consequences for entire populations and ecosystems.
• Fragmentation of habitat due to urban expansion
• Disruption of traditional migration routes
• Obstruction or disappearance of natural corridors for migration
• Increased vehicular traffic as a threat to migrating wildlife
• Pollution and noise pollution affecting animals’ behavior
• Artificial lights causing disorientation in nocturnal species
Role of geographical barriers in shaping migration routes
Geographical barriers play a pivotal role in shaping the migration routes of wildlife populations. Natural obstacles such as mountains, rivers, deserts, and oceans can act as formidable barriers, influencing the movement of species across different landscapes. These barriers can serve as physical boundaries, altering migration patterns by forcing animals to navigate around or adapt to the challenges posed by these features.
The presence of geographical barriers can lead to the isolation of certain populations, limiting gene flow and genetic diversity among species. This isolation can result in the formation of distinct subpopulations with unique genetic characteristics. Additionally, these barriers can create bottlenecks or choke points along migration routes, where animals may be more vulnerable to predation, habitat loss, or other threats. The interplay between geographical barriers and wildlife migration highlights the intricate relationship between the physical environment and the movement of species across vast territories.
• Geographical barriers such as mountains, rivers, deserts, and oceans influence wildlife migration routes
• These barriers act as physical boundaries altering migration patterns
• Isolation caused by geographical barriers can limit gene flow and genetic diversity among species
• Formation of distinct subpopulations with unique genetic characteristics due to isolation caused by barriers
• Geographical barriers create bottlenecks or choke points along migration routes where animals may be more vulnerable
Significance of conservation efforts in preserving migration corridors
Conservation efforts play a crucial role in safeguarding migration corridors for wildlife populations. Preserving these pathways ensures the uninterrupted movement of animals between their breeding, feeding, and resting grounds. By maintaining these routes, conservation efforts help prevent habitat fragmentation and promote genetic diversity among species.
Furthermore, protecting migration corridors aids in the conservation of entire ecosystems by allowing for the natural flow of energy and nutrients. As animals traverse these corridors, they contribute to seed dispersal, pollination, and predator-prey dynamics, which are essential for ecosystem health. By recognizing the significance of conservation efforts in preserving migration corridors, we can better understand the interconnectedness of species and habitats, leading to more effective conservation strategies.
• Conservation efforts help prevent habitat fragmentation
• Preserving migration corridors promotes genetic diversity among species
• Protecting migration corridors aids in the conservation of entire ecosystems
• Natural flow of energy and nutrients is maintained through protected migration corridors
• Animals contribute to seed dispersal, pollination, and predator-prey dynamics as they traverse these pathways