Understanding Topographic Lines
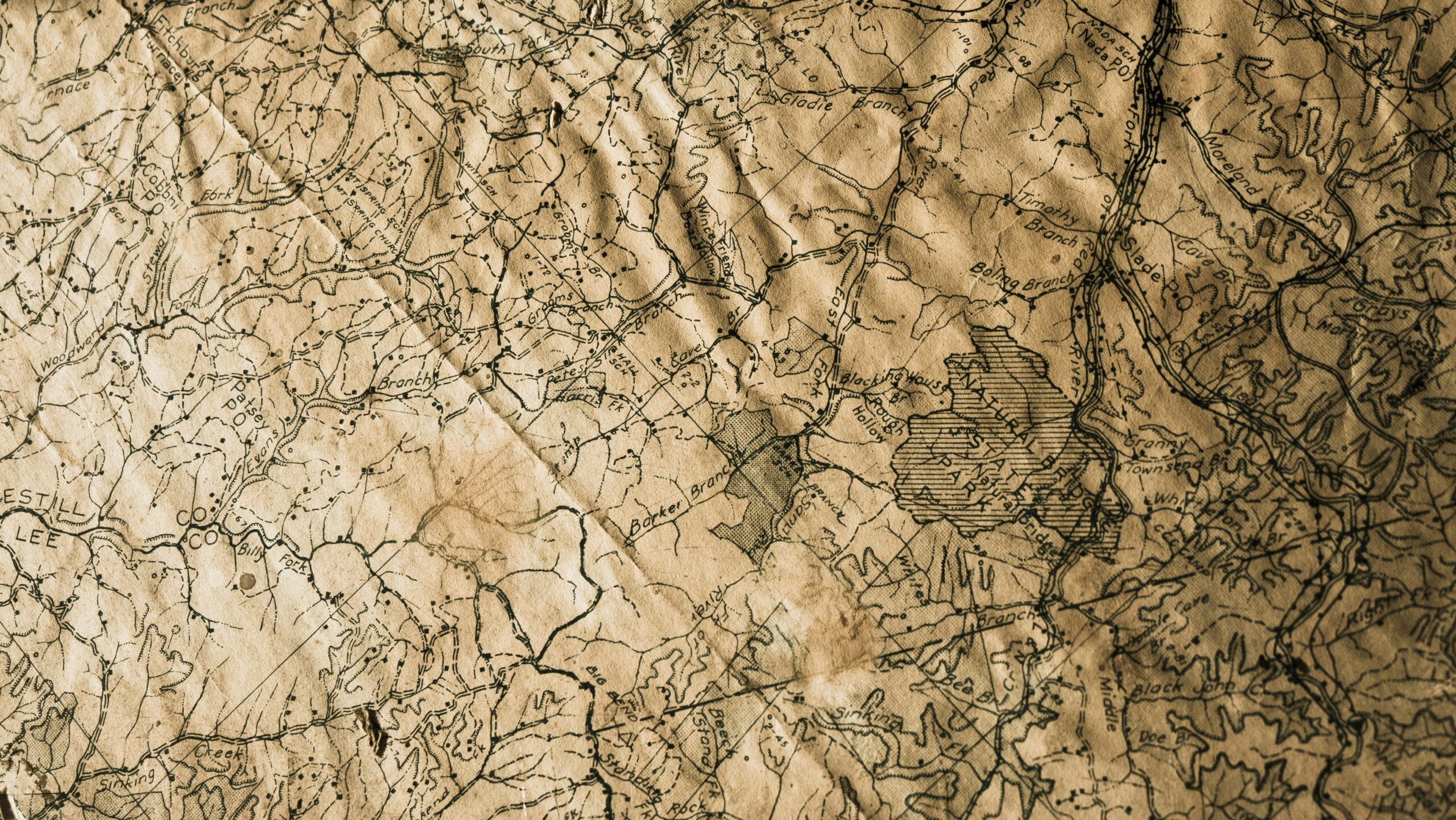
Topographic lines, also known as contour lines, are crucial elements on a map representing the elevation and shape of the land. These curved lines connect points of equal elevation above or below sea level. By closely examining the spacing and arrangement of these lines, one can gain valuable insight into the terrain’s topography, such as identifying valleys, hills, and even mountains.
Each contour line on a topographic map signifies a specific elevation, making it easier to visualize the landscape in three dimensions. Typically, these lines form concentric shapes, with smaller intervals indicating steeper terrain and larger intervals representing gradual slopes. By developing a keen eye for interpreting these contour lines, map readers can discern the elevation changes and understand the spatial relationship between different land features.
• Topographic lines, also known as contour lines, represent elevation and shape of land
• These curved lines connect points of equal elevation above or below sea level
• Examining spacing and arrangement provides insight into terrain’s topography
• Each contour line signifies a specific elevation on the map
• Concentric shapes with smaller intervals indicate steeper terrain while larger intervals represent gradual slopes
Identifying Elevation Changes
To identify elevation changes on a topographic map, begin by closely examining the contour lines. These lines connect points of equal elevation and reveal the ups and downs of the landscape. When contour lines are close together, it indicates a steep slope, whereas widely spaced lines indicate a gentle slope. By paying attention to the spacing and patterns of the contour lines, you can visualize the elevation variations across the terrain.
Moreover, understanding contour intervals is crucial in identifying elevation changes accurately. Contour intervals represent the vertical distance between each contour line, and this information helps determine the steepness of the terrain. A smaller contour interval signifies a more gradual slope, whereas a larger interval indicates a steeper incline. By analyzing the contour intervals in conjunction with the contour lines, you can gain a comprehensive insight into the elevation changes present on the topographic map.
• To identify elevation changes on a topographic map, closely examine the contour lines
• Close together contour lines indicate a steep slope, while widely spaced lines indicate a gentle slope
• Pay attention to spacing and patterns of contour lines to visualize elevation variations across terrain
• Understanding contour intervals is crucial in accurately identifying elevation changes
• Contour intervals represent vertical distance between each contour line
• Smaller interval signifies more gradual slope, larger interval indicates steeper incline
• Analyzing contour intervals with contour lines provides comprehensive insight into elevation changes on map
Reading Contour Intervals
To read contour intervals correctly, it’s essential to understand that these lines connect points of equal elevation on a topographic map. Each contour line represents a specific elevation above sea level, aiding in visualizing the shape of the land. By identifying contour lines that are close together, you can determine steep terrain, while lines spaced further apart indicate a more gradual slope.
Contour intervals help visualize the three-dimensional terrain on a two-dimensional map. By studying these lines and paying attention to their proximity and spacing, you can interpret the landscape’s features such as hills, valleys, and plateaus. Additionally, contour intervals provide crucial information about the elevation changes within a specific area, enabling you to navigate terrain with a better understanding of its topography.
• Contour lines connect points of equal elevation on a map
• Close contour lines indicate steep terrain
• Spaced out contour lines suggest a gradual slope
• Contour intervals help visualize three-dimensional terrain on a two-dimensional map
• Studying contour lines helps interpret landscape features like hills, valleys, and plateaus
• Understanding elevation changes within an area aids in navigating terrain
Recognizing Steep vs. Gentle Slopes
To distinguish between steep and gentle slopes on a topographic map, it is essential to pay attention to the spacing and shape of contour lines. Steep slopes are indicated by closely spaced contour lines, whereas gentle slopes are depicted by more widely spaced contour lines. The closer together the contour lines are, the steeper the slope. Conversely, when contour lines are spaced farther apart, it indicates a gradual incline.
In addition to contour line spacing, the shape of the contour lines can also provide valuable clues about the slope’s steepness. Contour lines that form tight circles or sharp bends suggest a steep slope, while contour lines that gradually curve and flow indicate a more gentle slope. By closely examining these visual cues on a topographic map, one can accurately identify and differentiate between steep and gentle slopes, aiding in navigation and understanding the terrain’s characteristics.
• Steep slopes are indicated by closely spaced contour lines
• Gentle slopes are depicted by more widely spaced contour lines
• The closer together the contour lines, the steeper the slope
• Contour lines that form tight circles or sharp bends suggest a steep slope
• Contour lines that gradually curve and flow indicate a gentle slope
Locating Peaks and Valleys
Peaks and valleys are key features that can be easily identified on a topographic map. Peaks are typically represented by a series of closely spaced contour lines forming a circular or oval shape. These lines indicate an area of higher elevation compared to its surroundings. Valleys, on the other hand, are depicted by V-shaped contour lines pointing towards higher elevations on either side. Valleys are often associated with water flow and can vary in depth and width, depending on the topography of the region.
Locating peaks and valleys on a topographic map can provide crucial information for outdoor enthusiasts, hikers, and geologists. By understanding the patterns of contour lines associated with peaks and valleys, individuals can anticipate the terrain’s ruggedness, plan their routes effectively, and gain insights into the geological history of the area. Peaks and valleys play a vital role in shaping landscapes and are essential components in deciphering topographic maps accurately.
• Peaks are represented by closely spaced contour lines forming a circular or oval shape
• Valleys are depicted by V-shaped contour lines pointing towards higher elevations on either side
• Valleys are often associated with water flow and can vary in depth and width
• Locating peaks and valleys on a topographic map is crucial for outdoor enthusiasts, hikers, and geologists
• Understanding the patterns of contour lines helps individuals anticipate terrain ruggedness and plan routes effectively
Interpreting Contour Shapes
Contour shapes on a topographic map provide valuable information about the terrain’s features. When contours form concentric circles, it usually indicates a hill or peak. The closer the contour lines are together, the steeper the slope. Conversely, widely spaced contours suggest a gentle slope or flat area. Pay attention to the direction and pattern of the contours to determine the shape of the land – whether it’s a ridge, valley, or plateau. Moreover, V-shaped contours can signify gullies or valleys, while U-shaped contours often represent ridge lines or saddles.
Contour shapes also reveal information about the landscape’s drainage patterns. Contour lines that form a series of closed loops may indicate a basin or depression, where water collects. These depressions are crucial to recognize when planning routes as they can impact travel and navigation. Additionally, “V” shapes with the point facing uphill typically indicate stream valleys or drainage channels, helping you identify how water flows through the area. By studying the various contour shapes on a topographic map, you can gain a better understanding of the land’s physical characteristics and make more informed decisions when exploring or navigating unfamiliar terrain.
• Contour shapes on a topographic map provide valuable information about the terrain’s features
• Concentric circles usually indicate a hill or peak
• Closer contour lines suggest steeper slopes, while widely spaced contours imply gentle slopes or flat areas
• Pay attention to the direction and pattern of contours to determine land shape – ridge, valley, plateau
• V-shaped contours may signify gullies or valleys; U-shaped contours often represent ridgelines or saddles
• Contour shapes also reveal information about landscape drainage patterns
• Closed loops can indicate basins or depressions where water collects
• Recognizing depressions is crucial for route planning as they impact travel and navigation
• “V” shapes facing uphill typically denote stream valleys or drainage channels
By studying various contour shapes on a topographic map, you can better understand the land’s physical characteristics and make informed decisions when exploring unfamiliar terrain.
Understanding Contour Line Spacing
Contour line spacing on a topographic map represents the vertical distance between each contour line. The spacing between contour lines indicates the steepness or gentleness of the terrain. Closer contour lines suggest a rapid change in elevation, indicating a steeper slope, while wider spacing between lines represents a more gradual incline. Understanding contour line spacing is crucial for accurately interpreting the elevation changes in an area and identifying the features of the landscape.
By paying attention to the contour line spacing on a topographic map, you can easily differentiate between flat areas and steep slopes. A closely spaced set of contour lines signifies a sharp change in elevation, such as a cliff or a ridge, while contours spread farther apart indicate a flatter terrain. Analyzing the contour line spacing in conjunction with the contour intervals can give you a clearer picture of the topography, allowing you to locate peaks, valleys, and other landforms with precision.
• Closer contour lines indicate a rapid change in elevation
• Wider spacing between lines represents a more gradual incline
• Closely spaced contour lines suggest a sharp change in elevation, like cliffs or ridges
• Contours spread farther apart indicate flatter terrain
• Analyzing contour line spacing with contour intervals helps locate peaks, valleys, and other landforms
Identifying Depressions and Hills
Depressions and hills are common features found on topographic maps that provide valuable information about the terrain. Depressions are represented by concentric contour lines with smaller values towards the center, illustrating areas of lower elevation surrounded by higher ground. Hills, on the other hand, are indicated by concentric contour lines with higher values towards the center, depicting areas of higher elevation compared to the surrounding terrain.
By carefully observing the contour lines surrounding depressions and hills, map readers can determine the depth and height of these features. Depressions with closely spaced contour lines suggest steep slopes, while wider spaced lines indicate gradual slopes. Similarly, hills with closely packed contour lines indicate a steep incline, whereas widely spaced lines reveal a more gentle slope. Understanding how to interpret these contour patterns is essential for accurately identifying and differentiating between depressions and hills on a topographic map.
• Depressions are represented by concentric contour lines with smaller values towards the center
• Hills are indicated by concentric contour lines with higher values towards the center
• Closely spaced contour lines around depressions suggest steep slopes
• Widely spaced lines around depressions indicate gradual slopes
• Closely packed contour lines on hills indicate a steep incline
• Widely spaced lines on hills reveal a more gentle slope
Determining Slope Direction
Slope direction can be determined by analyzing the spacing and orientation of contour lines on a topographic map. On a topographic map, contour lines that are closer together indicate a steeper slope, while lines that are further apart indicate a gentler slope. By observing the direction in which the contour lines bend and the pattern they create, one can ascertain the direction of the slope.
Additionally, slope direction can also be identified by looking at the lines of equal elevation on a topographic map. In general, these lines will form a V-shape pointing upstream on a hillside and downstream on a mountainside. By understanding these subtle cues and paying attention to the details of contour lines, hikers and outdoor enthusiasts can navigate their way through various terrains with ease and accuracy.
• Closer contour lines indicate a steeper slope
• Further apart contour lines indicate a gentler slope
• Observing the direction in which contour lines bend can determine slope direction
• Lines of equal elevation form a V-shape pointing upstream on a hillside and downstream on a mountainside
Recognizing Flat Areas
Flat areas on a topographic map are represented by closely spaced contour lines that are nearly parallel to each other. These flat sections are usually found on plains, plateaus, or gentle slopes where there is little to no change in elevation. When you come across contour lines that appear evenly spaced and run parallel to each other, this indicates a relatively flat terrain.
It is important to note that flat areas on a topographic map may still have slight variations in elevation, even though the contour lines are closely packed together. Therefore, when identifying flat areas, pay attention to the contour interval specified on the map to determine the degree of flatness. By recognizing and understanding flat areas on a topographic map, you can gain valuable insights into the terrain and plan your navigation accordingly.
• Flat areas on a topographic map are represented by closely spaced contour lines
• These flat sections are usually found on plains, plateaus, or gentle slopes
• Contour lines that are evenly spaced and parallel indicate a relatively flat terrain
• Flat areas may still have slight variations in elevation despite closely packed contour lines
• Pay attention to the contour interval specified on the map to determine the degree of flatness
Identifying Cliffs and Ridges
Cliffs and ridges are distinctive features that can be identified on a topographic map by closely examining the contour lines. Cliffs are represented by closely spaced contour lines that often form sharp, vertical edges on the map. These lines indicate a rapid change in elevation and can help hikers or climbers locate challenging terrain. Ridges, on the other hand, are depicted by contour lines that form a series of concentric circles, indicating a gradual rise in elevation along a distinct line. Identifying these features can be crucial for understanding the topography of an area and planning routes accordingly.
When locating cliffs and ridges on a map, it’s important to pay attention to how the contour lines interact with other features. Cliffs are often accompanied by steep slopes on one side and flat or gently sloping terrain on the other. Ridges, on the other hand, may connect multiple peaks or high points along a continuous line of higher elevation. By examining the arrangement of contour lines, outdoor enthusiasts can gain valuable insights into the terrain’s characteristics, such as elevation changes, slope steepness, and potential obstacles to navigate around.
• Cliffs are represented by closely spaced contour lines
• Contour lines form sharp, vertical edges on the map
• Rapid change in elevation indicated by cliff contour lines
• Ridges depicted by contour lines forming concentric circles
• Gradual rise in elevation along a distinct line shown by ridge contour lines
• Connecting multiple peaks or high points along a continuous line of higher elevation
Locating Water Features
Water features such as rivers, lakes, and streams play a crucial role in topographic maps. To locate these features, look for blue lines or symbols depicting water bodies on the map. Rivers are indicated by blue lines with arrows showing the direction of the flow, while lakes are represented by blue shapes. Streams are shown as thinner blue lines feeding into larger bodies of water. By identifying these water features on a topographic map, you can better understand the terrain and plan your route accordingly.
In addition to rivers and lakes, topographic maps also show other water-related features such as swamps, marshes, and ponds. These wetland areas are usually depicted with light blue shading or symbols to differentiate them from larger bodies of water. Paying attention to these smaller water features can help you navigate through diverse terrains and avoid obstacles during your outdoor adventures.
• Rivers are indicated by blue lines with arrows showing the direction of flow
• Lakes are represented by blue shapes on the map
• Streams are shown as thinner blue lines feeding into larger bodies of water
• Swamps, marshes, and ponds are depicted with light blue shading or symbols on the map
• Identifying these smaller water features can help navigate through diverse terrains
Understanding Map Scale
When working with a topographic map, understanding the scale is crucial for accurate interpretation and navigation. Map scale indicates the ratio between distances on the map and actual distances on the Earth’s surface. Common scales include 1:24,000, 1:50,000, and 1:100,000, with larger numbers indicating less detail but covering larger areas. For example, a map with a scale of 1:24,000 shows more detail than one with a scale of 1:100,000.
Map scales are typically represented as fractions or ratios, with the first number representing a unit of distance on the map and the second number indicating the equivalent distance on the ground. Understanding the scale allows you to calculate actual distances between locations, estimate hiking times, and determine the size of geographic features. Before using a topographic map, always identify and comprehend the scale to ensure accurate interpretation and use of the map’s information.
• Map scale indicates the ratio between distances on the map and actual distances on Earth’s surface
• Common scales include 1:24,000, 1:50,000, and 1:100,000
• Larger numbers indicate less detail but cover larger areas
• A map with a scale of 1:24,000 shows more detail than one with a scale of 1:100,000
Map scales are typically represented as fractions or ratios. The first number represents a unit of distance on the map while the second number indicates the equivalent distance on the ground. Understanding the scale is essential for calculating actual distances between locations, estimating hiking times accurately, and determining the size of geographic features.
Before using a topographic map for navigation or interpretation purposes, it is crucial to identify and comprehend its scale. This ensures that you can make accurate calculations and interpretations based on the information provided by the map.
Reading Grid Coordinates
To find a specific location on a map, grid coordinates are essential. The grid system divides the map into equally proportioned squares, with each square assigned a unique identifier based on its location. The horizontal lines are the east-west lines, while the vertical lines are the north-south lines. By using the intersections of these lines, you can pinpoint any location on the map accurately.
Each square on a map is further subdivided into smaller sections, making it easier to specify precise locations. For example, if you are given coordinates of A-3, it means you should locate square A on the horizontal line and count down to the third vertical line. Grid coordinates are crucial when navigating unfamiliar terrain or when providing specific location information to others.
• Grid coordinates are essential for finding specific locations on a map
• The grid system divides the map into equally proportioned squares
• Horizontal lines are east-west lines, while vertical lines are north-south lines
• Intersections of these lines help pinpoint any location accurately
Each square on a map is subdivided into smaller sections to specify precise locations. For example, if given coordinates of A-3, locate square A on the horizontal line and count down to the third vertical line. Grid coordinates play a vital role in navigating unfamiliar terrain or providing specific location information to others.
Using Legend and Symbols
When reading a topographic map, understanding the legend and symbols is essential for interpreting the features represented on the map accurately. The legend contains key information about the meaning of different symbols used on the map, such as contour lines, vegetation, water bodies, roads, and more. By referring to the legend, map readers can easily identify various elements depicted on the map and understand their significance in the terrain. Additionally, symbols on a topographic map provide important details about the landscape, helping users navigate and comprehend the geographical characteristics of the area they are exploring.
Symbols on a topographic map are designed to be concise yet informative, offering a visual representation of different features in a simplified manner. Each symbol conveys specific information about the terrain, infrastructure, or natural elements present in the mapped area. By familiarizing oneself with the symbols commonly used on topographic maps, individuals can enhance their map-reading skills and gain a deeper understanding of the layout and characteristics of the land. Paying attention to details like symbols can make navigation more efficient and enable users to make informed decisions while exploring unfamiliar territories.
• Topographic maps contain key information in the legend about various symbols used on the map
• Symbols represent features such as contour lines, vegetation, water bodies, and roads
• Understanding symbols helps map readers identify elements on the map accurately
• Symbols provide important details about the landscape for navigation and comprehension
• Each symbol conveys specific information about terrain, infrastructure, or natural elements
• Familiarizing oneself with symbols enhances map-reading skills and understanding of the land layout
• Paying attention to symbols can make navigation more efficient and aid in making informed decisions while exploring
Interpreting Topographic Profiles
Generate a Topographic Profile, a graphic representation of a vertical cross-section of the Earth’s surface along a specific line, helps users visualize the elevation changes and terrain features within a region. By interpreting the profile, one can identify variations in elevation, determine the steepness of slopes, locate peaks and valleys, and anticipate possible challenges or advantages when navigating through the area. The profile provides valuable insights into the topography and helps users understand the three-dimensional layout of the landscape in a two-dimensional format.
When examining a Topographic Profile, each line represents a specific elevation on the terrain, allowing users to easily distinguish between high and low points. The closer the lines are together, the steeper the slope, indicating a rapid change in elevation over a short distance. By analyzing the spacing and pattern of the contour lines on the profile, one can identify the overall slope direction and assess the level of difficulty that may be encountered when traversing the area. Additionally, peaks, valleys, cliffs, ridges, and other prominent landforms are clearly depicted on the profile, aiding users in navigation and route planning.
• Topographic Profiles provide a visual representation of elevation changes
• Helps in identifying variations in elevation and steepness of slopes
• Allows users to locate peaks, valleys, cliffs, and other terrain features
• Assists in understanding the three-dimensional layout of the landscape in a two-dimensional format
When analyzing a Topographic Profile:
• Each line represents a specific elevation on the terrain
• Closer lines indicate steeper slopes with rapid changes in elevation
• Spacing and pattern of contour lines help identify slope direction and level of difficulty
• Prominent landforms such as peaks, valleys, ridges are clearly depicted
Understanding Map Orientation
When using a topographic map for navigation or planning outdoor activities, understanding map orientation is crucial. The orientation of a map indicates the relationship between the features on the map and their corresponding positions on the Earth’s surface. Most maps are oriented with north at the top, allowing users to align the map with the actual terrain they are navigating.
Having a clear understanding of map orientation helps in interpreting the geographic features accurately. By recognizing the cardinal directions on a map, users can orient themselves and navigate terrain effectively. Whether hiking in the wilderness or studying a map for geographical analysis, being able to read the map with the correct orientation is fundamental for successful map reading and interpretation.
• Understanding map orientation is crucial for navigation and planning outdoor activities
• Most maps are oriented with north at the top
• Clear understanding of map orientation helps in interpreting geographic features accurately
• Recognizing cardinal directions on a map helps in orienting oneself and navigating terrain effectively
• Reading the map with correct orientation is fundamental for successful map reading and interpretation
Recognizing Geographic Features
Identifying geographic features on a topographic map is essential for understanding the terrain depicted. By examining the contour lines, you can locate prominent landforms such as mountains, valleys, and plateaus. Peaks are often represented by concentric circles, while valleys are depicted by V-shaped contour lines. Understanding how to differentiate between these features allows for better navigation and interpretation of the map.
Additionally, rivers, lakes, and other water bodies can be identified on a topographic map by blue lines or shading. These features are crucial for planning outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, or fishing. By recognizing the presence of water bodies on the map, you can also infer the direction of flow and potential obstacles along your route.
• Peaks are often represented by concentric circles
• Valleys are depicted by V-shaped contour lines
• Rivers, lakes, and other water bodies can be identified by blue lines or shading
• Recognizing water bodies on the map helps infer direction of flow and potential obstacles
Identifying Landforms and Terrain Types
Topographic maps provide valuable information for identifying various landforms and terrain types. By closely examining the contour lines on the map, one can pinpoint different geographical features such as valleys, hills, plateaus, and mountains. The spacing and shape of contour lines can offer insights into the steepness or gentleness of slopes, allowing map users to visualize the topography of the area accurately.
Moreover, through the analysis of contour intervals and elevation changes, individuals can distinguish between flat areas, cliffs, ridges, and depressions on a topographic map. Understanding how elevation levels shift across the landscape enables map readers to interpret the terrain types present in the area. By effectively utilizing the legend and symbols provided on the map, users can enhance their comprehension of the landforms and terrain features illustrated, aiding navigation and exploration of the region depicted.
• Topographic maps provide valuable information for identifying various landforms and terrain types
• Examining contour lines on the map can pinpoint geographical features such as valleys, hills, plateaus, and mountains
• Spacing and shape of contour lines offer insights into the steepness or gentleness of slopes
• Analysis of contour intervals and elevation changes helps distinguish between flat areas, cliffs, ridges, and depressions on a topographic map
• Understanding how elevation levels shift across the landscape enables interpretation of terrain types present in the area
• Effective utilization of legend and symbols provided on the map enhances comprehension of landforms and terrain features illustrated
Using Topographic Maps for Navigation
Topographic maps are essential tools for navigation in outdoor environments, providing detailed information about the geographical features of a particular area. By understanding how to read these maps effectively, hikers, climbers, and adventurers can plan routes, identify landmarks, and stay oriented in unfamiliar terrain. Contour lines on a topographic map can indicate elevation changes, helping users visualize the steepness of slopes and locate high and low points in the landscape.
In addition to contour lines, topographic maps also feature symbols and legends that represent natural and man-made features such as rivers, roads, and buildings. By familiarizing themselves with these symbols and understanding the scale of the map, navigators can pinpoint their location, plan efficient routes, and avoid getting lost in the wilderness. Learning how to interpret topographic profiles, grid coordinates, and other key elements of these maps can greatly enhance one’s ability to navigate confidently and safely in any outdoor setting.
• Topographic maps provide detailed information about geographical features
• Contour lines indicate elevation changes and steepness of slopes
• Symbols and legends represent natural and man-made features like rivers, roads, and buildings
• Understanding scale helps pinpoint location and plan efficient routes
• Interpreting topographic profiles, grid coordinates enhances navigation ability