Coral reef structures and formation
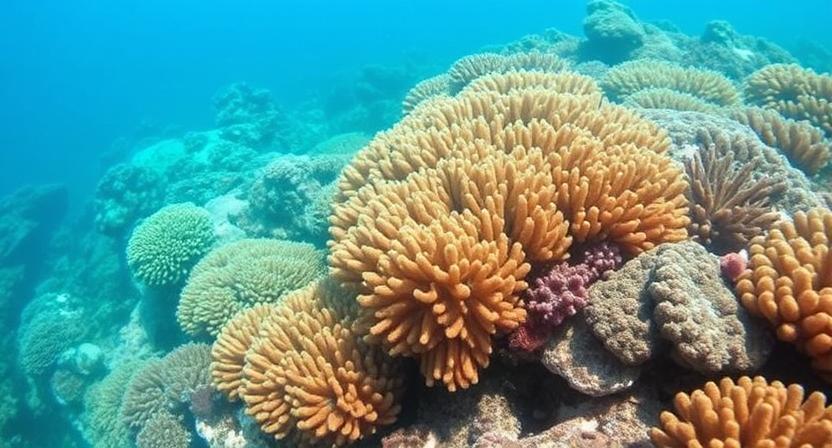
One of the most fascinating aspects of coral reefs is the intricate structures they form underwater. These structures are created by the accumulation of calcium carbonate skeletons produced by the coral polyps over time. As more and more coral colonies grow and die, their skeletons build upon each other, eventually forming vast and diverse reef systems. The branching, massive, and encrusting formations of coral reefs provide essential habitats for a myriad of marine life, making them some of the most biologically diverse ecosystems on the planet.
Coral reefs mainly develop in clear, warm, shallow waters where there is an abundance of sunlight to support the photosynthetic algae living within the coral tissues. These algae, known as zooxanthellae, provide the coral with essential nutrients through photosynthesis, aiding in the calcification process that contributes to reef structure formation. The symbiotic relationship between the coral polyps and the zooxanthellae is crucial for the health and growth of coral reefs. The incredible diversity of shapes and sizes of coral reef structures not only creates a visually stunning underwater landscape but also plays a vital role in supporting marine biodiversity and ecosystem functioning.
• Coral reefs are formed by the accumulation of calcium carbonate skeletons produced by coral polyps
• The branching, massive, and encrusting formations of coral reefs provide essential habitats for marine life
• Coral reefs develop in clear, warm, shallow waters with abundant sunlight to support photosynthetic algae
• Zooxanthellae algae living within coral tissues provide nutrients through photosynthesis for reef formation
• Symbiotic relationship between coral polyps and zooxanthellae is crucial for health and growth of coral reefs
The role of coral reefs in coastal protection
Coral reefs play a crucial role in protecting coastal areas from the impacts of waves and currents. The intricate structure of coral reefs acts as a physical barrier, reducing the energy and force of incoming waves, thereby helping to prevent coastal erosion and flooding. The presence of healthy coral reefs along coastlines contributes significantly to stabilizing the shoreline and safeguarding the surrounding land from erosion.
Furthermore, coral reefs are effective in absorbing wave energy, dissipating it across the reef structure and reducing its intensity before reaching the shore. This absorption of wave energy by coral reefs not only protects the immediate coastal areas but also helps in preserving beaches and sand dunes by preventing excessive erosion. The natural resilience of coral reefs in withstanding wave action showcases their significance in coastal protection and underscores the need for their conservation and preservation.
• Coral reefs act as a physical barrier, reducing the energy and force of incoming waves
• Helps prevent coastal erosion and flooding
• Contributes to stabilizing the shoreline and safeguarding surrounding land from erosion
• Absorbs wave energy, dissipating it across the reef structure
• Reduces intensity of waves before reaching shore
• Protects beaches and sand dunes from excessive erosion
• Demonstrates natural resilience in withstanding wave action
The physical barrier provided by coral reefs against waves and currents
Coral reefs act as a natural defense against the relentless forces of waves and currents that batter coastal areas. Their intricate structures, made up of calcium carbonate exoskeletons secreted by coral polyps, form a formidable barrier that helps dissipate the energy of incoming waves. This barrier reduces the impact of wave action on shorelines, thereby protecting coastal habitats and infrastructure from erosion and damage.
In addition to mitigating wave energy, coral reefs also play a crucial role in altering currents along the shoreline. As waves encounter the reef structure, they are deflected and refracted, causing the currents to flow around the reef rather than directly towards the coast. This redirection of currents helps to prevent sediment erosion and maintains the stability of the coastline. By effectively slowing down the movement of water, coral reefs aid in maintaining the delicate balance of coastal ecosystems and contribute to the overall resilience of coastal areas against natural hazards.
• Coral reefs act as a natural defense against waves and currents
• The intricate structures of coral reefs made up of calcium carbonate exoskeletons form a barrier
• This barrier helps dissipate the energy of incoming waves, reducing their impact on shorelines
• Coral reefs alter currents along the shoreline by deflecting and refracting waves
• Redirection of currents around the reef prevents sediment erosion and maintains coastline stability
• Coral reefs aid in maintaining the delicate balance of coastal ecosystems
The absorption of wave energy by coral reef structures
Coral reef structures play a crucial role in absorbing wave energy along coastlines. As waves approach the reef, they break against the complex structure of the coral, dispersing their energy. This absorption helps to reduce the force of the waves reaching the shore, thereby protecting coastal areas from erosion and damage. The intricate composition of the coral reef provides a natural defense mechanism against the power of incoming waves, mitigating the impact on the surrounding ecosystem.
In addition to safeguarding coastal regions, the absorption of wave energy by coral reefs also contributes to the maintenance of the delicate balance within the marine environment. By dissipating wave energy, coral reefs create calmer waters in their vicinity, which is beneficial for the growth and survival of various marine species. The ability of coral reefs to absorb wave energy not only protects coastal communities but also supports the biodiversity and ecological health of the surrounding marine habitats.
• Coral reef structures break waves and absorb their energy
• Helps reduce force of waves reaching the shore, preventing erosion
• Natural defense mechanism against incoming waves
• Maintains balance in marine environment by creating calmer waters near reefs
• Supports growth and survival of marine species
• Protects coastal communities and supports biodiversity in surrounding habitats
How coral reefs reduce erosion by stabilizing coastlines
Coral reefs play a crucial role in reducing erosion and stabilizing coastlines. The intricate structure of coral reefs acts as a natural barrier, absorbing the force of waves and currents that would otherwise erode the shore. This buffering effect helps to protect coastal areas from the relentless impact of the sea, preserving the integrity of the coastline and preventing land loss.
Furthermore, coral reefs contribute to shoreline stability by trapping sediment and promoting sand accumulation. The calcium carbonate skeletons of coral provide a solid foundation for the buildup of sediment, which in turn helps to maintain the natural balance of sand along beaches. This process of sediment retention and sand supply not only supports the health of the coral reef ecosystem but also safeguards coastal regions from erosion, highlighting the invaluable role that coral reefs play in protecting shorelines worldwide.
• Coral reefs act as a natural barrier, absorbing the force of waves and currents
• This buffering effect helps protect coastal areas from erosion
• Coral reefs trap sediment and promote sand accumulation
• The calcium carbonate skeletons of coral provide a solid foundation for sediment buildup
• Sediment retention and sand supply support the health of coral reef ecosystems
The importance of healthy coral reefs in protecting coastal areas
Healthy coral reefs play a crucial role in safeguarding coastal areas from various threats. These vibrant ecosystems act as natural barriers that help protect shorelines from the erosive forces of waves and currents. By absorbing wave energy and stabilizing coastlines, coral reefs aid in reducing erosion and preventing land loss along the coast.
Additionally, coral reefs play a vital role in buffering against storm surges, acting as a first line of defense for coastal communities and infrastructure. Their ability to maintain sand supply to beaches helps in preserving the natural environment and supports beach nourishment efforts. Overall, the presence of healthy coral reefs contributes significantly to coastal resilience and underscores the importance of their conservation for the benefit of both marine ecosystems and human populations.
• Healthy coral reefs act as natural barriers protecting shorelines from erosive forces
• Coral reefs absorb wave energy and stabilize coastlines, reducing erosion and preventing land loss
• Coral reefs buffer against storm surges, serving as a first line of defense for coastal communities and infrastructure
• Maintaining sand supply to beaches helps preserve the natural environment and supports beach nourishment efforts
The relationship between coral reefs and beach nourishment
Coral reefs play a crucial role in beach nourishment by providing a natural source of sand for coastal areas. The intricate structures of coral reefs act as barriers, trapping sediment and creating suitable habitats for sand-producing organisms. As waves break against the reef, they help to erode and break down the coral skeletons, contributing to the formation of sand that is then transported along the coast through natural processes.
The presence of healthy coral reefs is essential for maintaining the sand supply to beaches, as they act as suppliers and protectors of this valuable resource. Without coral reefs, the natural flow of sand to shorelines would be disrupted, leading to erosion and coastal degradation. Additionally, coral reefs support a diverse ecosystem of marine life that contributes to the overall health and resilience of coastal areas.
• Coral reefs act as barriers, trapping sediment and creating habitats for sand-producing organisms
• Waves breaking against coral reefs erode and break down coral skeletons, contributing to the formation of sand
• Healthy coral reefs are essential for maintaining the sand supply to beaches and preventing erosion
• Coral reefs support a diverse ecosystem of marine life that contributes to the health and resilience of coastal areas
The impact of coral reef degradation on coastal erosion
Coral reef degradation significantly exacerbates coastal erosion, jeopardizing the stability of shorelines and the protection of coastal communities. As coral reefs deteriorate, their ability to absorb wave energy diminishes, leaving the coast susceptible to the full force of waves and currents. Without the natural buffer provided by healthy reefs, erosion rates increase, leading to the loss of valuable coastal land and infrastructure.
The intricate relationship between coral reefs and coastal protection underscores the critical importance of conserving these ecosystems. As coral reefs decline, the coastal areas they once shielded face heightened risks of erosion and inundation. Recognizing the vital role that coral reefs play in safeguarding coastlines highlights the urgent need for conservation efforts to preserve these invaluable natural defenses.
• Coral reef degradation leads to increased coastal erosion
• Diminished ability of degraded reefs to absorb wave energy
• Loss of natural buffer increases erosion rates and threatens coastal land and infrastructure
• Conservation of coral reefs is crucial for protecting coastlines from erosion and inundation
• Urgent need for conservation efforts to preserve coral reefs as natural defenses against coastal erosion
The ability of coral reefs to buffer against storm surges
Coral reefs play a crucial role in coastal protection by acting as natural barriers against storm surges. When strong waves and currents approach the coastline during storms, the intricate structures of coral reefs help to dissipate the energy of these powerful forces. This buffering effect reduces the impact of storm surges on coastal areas, helping to safeguard not only the reefs themselves but also the surrounding communities and ecosystems.
In addition to providing physical protection, coral reefs also contribute to the overall resilience of coastal areas by absorbing and deflecting the force of incoming waves. This process helps to prevent erosion of the coastline and maintain the stability of the shoreline. By serving as a natural defense mechanism, coral reefs mitigate the destructive effects of storm surges and contribute to the long-term sustainability of coastal environments.
• Coral reefs act as natural barriers against storm surges
• Intricate structures help dissipate energy of strong waves and currents
• Buffering effect reduces impact of storms on coastal areas
• Safeguards reefs, surrounding communities, and ecosystems
• Coral reefs contribute to overall resilience of coastal areas
• Absorb and deflect force of incoming waves
• Prevent erosion of coastline and maintain shoreline stability
• Serve as natural defense mechanism against storm surges
The role of coral reefs in maintaining sand supply to beaches
Coral reefs play a crucial role in maintaining the sand supply to beaches. As waves break over the reefs, they help to break down corals and other hard structures, creating sand. This sand is then transported by currents and waves towards the shore, replenishing beaches and contributing to shoreline stability. Without healthy coral reefs, this natural process of sand production and transport would be significantly disrupted, leading to beach erosion and loss of valuable coastal land.
Furthermore, the complex structure of coral reefs provides habitats for various marine species, including those that play a role in the formation and maintenance of sand on beaches. For instance, certain types of fish that dwell in coral reef ecosystems help in the production of sand by excreting calcium carbonate, a key component of sand. By supporting a diverse array of organisms that contribute to the overall ecosystem functioning, coral reefs indirectly aid in the continuous supply of sand to beaches, highlighting their importance in preserving coastal areas for both ecological and recreational purposes.
• Coral reefs break down corals and hard structures to create sand
• Sand is transported by currents and waves towards the shore
• Replenishes beaches and contributes to shoreline stability
• Without healthy coral reefs, beach erosion would occur
• Coral reef habitats support marine species that aid in sand production
• Fish excrete calcium carbonate, a key component of sand
• Diverse array of organisms contribute to ecosystem functioning
The connection between coral reefs and the prevention of land loss
Coral reefs play a crucial role in preventing land loss along coastlines. These intricate ecosystems act as natural barriers, absorbing the force of waves and currents that erode shores. Through their structural complexity and biological processes, coral reefs help to dissipate wave energy, reducing the impact on coastal areas. As waves break against the reef, their energy is dispersed, protecting the land behind from erosion.
Furthermore, coral reefs contribute to the stabilization of coastlines by trapping sediments and promoting the accumulation of sand. This sediment retention helps to build and maintain beaches, which are vital for protecting coastal land from being lost to the sea. The intricate relationship between coral reefs and the prevention of land loss highlights the importance of preserving these fragile ecosystems for the long-term resilience of coastal communities.
• Coral reefs act as natural barriers against waves and currents
• They absorb the force of waves, reducing erosion along coastlines
• The structural complexity helps dissipate wave energy, protecting coastal areas
• Coral reefs trap sediments and promote sand accumulation for beach stabilization
• Beaches are vital for protecting coastal land from being lost to the sea
The significance of coral reefs in protecting infrastructure along coastlines
Coral reefs play a vital role in safeguarding infrastructure along coastlines. The structures of healthy reefs provide a natural barrier that helps reduce the impact of waves and storms on coastal buildings, roads, and other essential facilities. By absorbing wave energy and dissipating the force of currents, coral reefs act as a protective shield, shielding coastal infrastructure from erosion and damage. This buffering effect not only protects human-made structures but also helps preserve the integrity of coastal ecosystems.
Furthermore, coral reefs contribute to maintaining the stability of shorelines, which is crucial for safeguarding infrastructure against coastal erosion. The intricate network of living organisms within coral reefs helps bind sediments and prevent them from being washed away by tides and currents. As a result, coral reefs play a critical role in preventing land loss and maintaining the natural dynamics of coastal areas. Protecting and preserving these valuable ecosystems is essential for ensuring the long-term resilience of coastal infrastructure against the threats posed by rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
• Coral reefs act as a natural barrier against waves and storms
• They absorb wave energy and dissipate currents, protecting coastal infrastructure
• Coral reefs help prevent erosion and damage to buildings, roads, and other facilities
• The stability of shorelines is maintained by coral reefs, preventing land loss
• Preserving coral reefs is crucial for the resilience of coastal infrastructure against rising sea levels and extreme weather events
The economic value of coral reefs in coastal protection
Coral reefs play a crucial role in coastal protection by acting as natural barriers that absorb wave energy and reduce erosion along shorelines. These vibrant ecosystems not only support a vast array of marine life but also provide invaluable services in safeguarding coastal communities and infrastructure. The economic value of coral reefs in coastal protection extends beyond their ecological significance, as they contribute significantly to the tourism industry and local economies.
Studies have shown that healthy coral reefs can save billions of dollars in damage costs caused by storms and erosion. By investing in the conservation and restoration of coral reefs, coastal regions can enhance their resilience to climate change impacts and mitigate the risks of coastal hazards. Recognizing the economic importance of coral reefs in coastal protection is essential for promoting sustainable practices and ensuring the long-term health of these valuable ecosystems.
• Coral reefs act as natural barriers that absorb wave energy and reduce erosion along shorelines
• They support a vast array of marine life and provide invaluable services in safeguarding coastal communities and infrastructure
• Healthy coral reefs can save billions of dollars in damage costs caused by storms and erosion
• Investing in the conservation and restoration of coral reefs can enhance resilience to climate change impacts
and mitigate risks of coastal hazards
• Recognizing the economic importance of coral reefs is essential for promoting sustainable practices
The contribution of coral reefs to overall coastal resilience
Coral reefs play a vital role in bolstering coastal resilience against natural disasters. These intricate ecosystems act as natural barriers, absorbing the impact of waves and currents, which helps in reducing coastal erosion and protecting shorelines. By dissipating wave energy, coral reefs effectively shield coastal communities from the full brunt of storm surges, minimizing the potential for damage to infrastructure and habitats along the coast.
Moreover, the presence of healthy coral reefs ensures the maintenance of sand supplies to beaches, thereby supporting the natural processes that contribute to coastal protection. As coral reefs work in tandem with the shoreline, they aid in stabilizing coastlines and preventing land loss due to erosion. Their significance in enhancing coastal resilience cannot be overstated, highlighting the essential need for their conservation and restoration to safeguard vulnerable coastal areas from the increasing risks posed by climate change and human activities.
• Coral reefs act as natural barriers, absorbing wave energy and currents
• They reduce coastal erosion and protect shorelines from damage
• Coral reefs minimize the impact of storm surges on coastal communities
• Healthy coral reefs maintain sand supplies to beaches, supporting natural processes for coastal protection
• Coral reefs stabilize coastlines and prevent land loss due to erosion
The comparison between natural coral reef protection and man-made structures
Natural coral reef protection and man-made structures represent two distinct approaches to coastal defense. Coral reefs are intricate ecosystems that have evolved over centuries to provide natural protection to coastlines. These living structures serve as a physical barrier, absorbing wave energy and reducing erosion by stabilizing shorelines. In contrast, man-made structures such as seawalls and breakwaters are designed and constructed to mimic the protective functions of coral reefs. While these structures can provide effective coastal protection, they lack the biodiversity and ecosystem services that coral reefs offer.
The effectiveness of coral reef protection compared to man-made structures is often a topic of debate among researchers and environmentalists. Natural coral reefs have the advantage of being dynamic, self-sustaining systems that can adapt to changing environmental conditions. In contrast, man-made structures require ongoing maintenance and can be costly to build and maintain. Additionally, coral reefs contribute to overall coastal resilience by buffering against storm surges and maintaining sand supply to beaches, functions that man-made structures may not fully replicate.
• Natural coral reefs are dynamic, self-sustaining systems
• Man-made structures require ongoing maintenance
• Coral reefs contribute to overall coastal resilience by buffering against storm surges
• Man-made structures may not fully replicate the functions of coral reefs
Natural coral reef protection and man-made structures both have their advantages and disadvantages when it comes to coastal defense. While natural coral reefs offer unique ecosystem services and adaptability, man-made structures provide a more controlled and predictable form of protection. Ultimately, the choice between these two approaches depends on factors such as cost, environmental impact, and long-term sustainability. Researchers continue to study the effectiveness of both methods in order to find the best solutions for protecting coastlines in an ever-changing world.
The effectiveness of coral reefs in reducing erosion compared to other methods
Coral reefs are highly effective in reducing erosion along coastlines compared to other methods. The intricate structure of coral reefs provides a natural barrier that helps dissipate wave energy and protect the shoreline from the erosive forces of waves and currents. In contrast to hard structures like seawalls and breakwaters, coral reefs not only reduce erosion but also support biodiversity and provide habitat for marine life, contributing to overall coastal ecosystem health.
Furthermore, coral reefs play a vital role in maintaining sand supply to beaches through the process of bioerosion and sediment production. This natural sediment transport helps nourish coastal areas and build up shorelines, enhancing their resilience to erosion. In comparison, artificial beach nourishment projects can be costly and may have limited effectiveness in the long term, whereas healthy coral reefs provide sustainable and ecologically beneficial solutions for reducing erosion and protecting coastal areas.
• Coral reefs provide a natural barrier that dissipates wave energy
• Support biodiversity and provide habitat for marine life
• Maintain sand supply to beaches through bioerosion and sediment production
• Enhance resilience to erosion and protect coastal areas in a sustainable manner
The challenges facing coral reefs and coastal protection efforts
Coral reefs face numerous challenges that impact their ability to provide coastal protection. Climate change poses a significant threat, leading to rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification, which can result in coral bleaching and reduced reef growth. Human activities such as overfishing, pollution, and coastal development also contribute to the degradation of coral reefs, weakening their natural defense mechanisms against erosion and storm surges.
Additionally, the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events due to climate change further test the resilience of coral reefs in protecting coastal areas. As coral reefs continue to face these challenges, there is a growing urgency to implement effective conservation and restoration efforts to preserve the vital role they play in coastal protection. Failure to address these issues could have detrimental impacts on the stability and resilience of coastal regions worldwide.
• Rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification from climate change
• Coral bleaching and reduced reef growth
• Overfishing, pollution, and coastal development from human activities
• Weakening natural defense mechanisms against erosion and storm surges
The challenges facing coral reefs highlight the need for immediate action to protect these vital ecosystems. Conservation efforts must focus on addressing the root causes of coral reef degradation, such as reducing carbon emissions and implementing sustainable fishing practices. Restoration projects can also help revive damaged reefs and enhance their ability to provide coastal protection.
• Implementing effective conservation measures
• Addressing root causes of coral reef degradation
• Reviving damaged reefs through restoration projects
As we confront the threats facing coral reefs, it is essential to recognize their critical role in safeguarding coastal communities from natural disasters. By prioritizing the preservation of these ecosystems, we can ensure the long-term resilience of coastal regions around the world. It is crucial that governments, organizations, and individuals work together to overcome these challenges and secure a sustainable future for coral reefs and coastal protection efforts.
• Recognizing critical role in safeguarding coastal communities
• Prioritizing preservation for long-term resilience
• Collaborating across sectors for sustainable future
The need for conservation and restoration of coral reefs to maintain coastal protection
Coral reefs play a crucial role in providing natural coastal protection by acting as physical barriers against waves and currents. The intricate structures of coral reefs help absorb wave energy, reducing the impact of erosion on coastlines. Healthy coral reefs are essential in stabilizing coastal areas and preventing land loss by maintaining the natural supply of sand to beaches.
The degradation of coral reefs poses a significant threat to coastal erosion, as weakened coral structures are less effective in buffering against storm surges. Without adequate conservation and restoration efforts, the loss of coral reefs could lead to increased vulnerability of coastal areas to erosion and infrastructure damage. It is imperative to recognize the importance of coral reefs in coastal protection and take action to preserve these valuable ecosystems for the resilience of coastal communities.
• Coral reefs act as physical barriers against waves and currents
• Intricate structures of coral reefs help absorb wave energy
• Healthy coral reefs stabilize coastal areas and prevent land loss by supplying sand to beaches
• Degradation of coral reefs increases vulnerability to erosion and infrastructure damage
• Conservation and restoration efforts are essential for preserving coral reefs
• Importance of coral reefs in coastal protection must be recognized
• Action is needed to preserve these ecosystems for the resilience of coastal communities
The potential future threats to coastal areas without healthy coral reefs
Without healthy coral reefs, coastal areas face serious threats to their resilience and protection. The degradation of coral reefs can result in increased coastal erosion due to the loss of natural barriers that help dissipate wave energy. This erosion can lead to the loss of valuable coastline, putting infrastructure and communities at risk of damage from storm surges and sea-level rise.
Furthermore, without the presence of healthy coral reefs, coastal areas may experience a decline in sand supply to beaches, leading to beach erosion and diminishing recreational and economic opportunities. The intricate relationship between coral reefs and beach nourishment is crucial for maintaining the dynamic equilibrium of coastal ecosystems. As coral reefs continue to face challenges from climate change, pollution, and unsustainable human activities, the future of coastal areas without their protective services remains uncertain.
• The degradation of coral reefs can result in increased coastal erosion
• Loss of natural barriers that help dissipate wave energy
• Risk of damage from storm surges and sea-level rise
• Decline in sand supply to beaches without healthy coral reefs
• Beach erosion leading to diminishing recreational and economic opportunities
The call to action for protecting and preserving coral reefs for coastal resilience.
Coral reefs play a crucial role in protecting coastal areas from erosion and storm surges. Their intricate structures act as natural barriers, absorbing wave energy and reducing the impact of currents along shorelines. Without healthy coral reefs, coastal communities are more vulnerable to land loss and damage to infrastructure. It is imperative that we prioritize the conservation and restoration of coral reefs to maintain their protective function and enhance coastal resilience.
As climate change continues to threaten marine ecosystems, the future of coral reefs hangs in the balance. Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and pollution are all contributing to the degradation of these vital habitats. To safeguard coastal areas and ensure their long-term protection, concerted efforts are needed to address these threats and support the resilience of coral reefs. It is time for collective action to preserve these ecosystems and secure the safety and sustainability of our coastal regions.
• Coral reefs act as natural barriers, reducing the impact of currents and waves along shorelines.
• Without healthy coral reefs, coastal communities are at a higher risk of land loss and infrastructure damage.
• Conservation and restoration efforts for coral reefs are essential to enhance coastal resilience.
As climate change poses a significant threat to marine ecosystems, including coral reefs, urgent action is required to address these challenges. Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and pollution are all contributing factors leading to the deterioration of coral reef health. To protect coastal areas from erosion and storm surges, it is crucial to focus on preserving these vital habitats through collaborative initiatives aimed at enhancing their resilience. The time has come for us to unite in our commitment towards safeguarding coral reefs for the benefit of both marine life and coastal communities.
• Climate change threatens the future of coral reefs through rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification.
• Collective efforts are needed to combat threats facing coral reef ecosystems.
• Preserving coral reefs is essential for ensuring the safety and sustainability of coastal regions.