Factors influencing changes in geographic landscapes
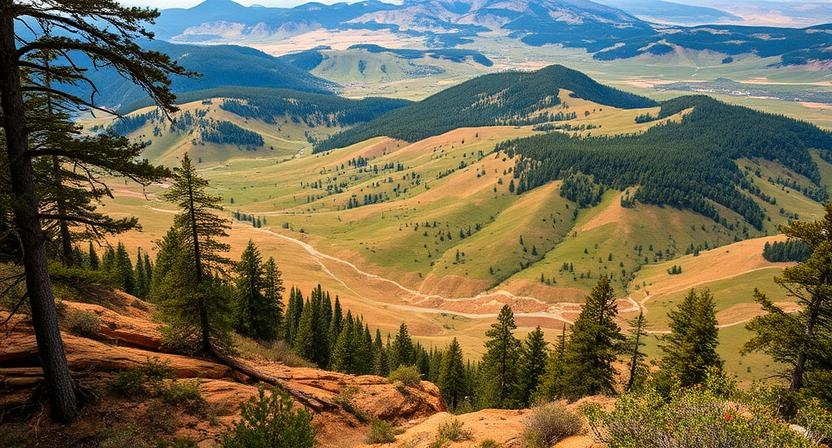

The dynamic nature of geographic landscapes is influenced by a myriad of factors that shape the Earth’s surface. Natural forces such as tectonic plate movements, volcanic eruptions, and erosion processes play a significant role in reshaping landforms over time. Additionally, climatic conditions such as temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns contribute to the evolution of geographic features, influencing everything from desert formations to glacier movements.
Human activities also have a profound impact on changing geographic landscapes. Urbanization, deforestation, agriculture, industrialization, and mining activities alter the natural terrain and can lead to soil degradation, habitat loss, and changes in biodiversity. Land development for transportation infrastructure, urban sprawl, and energy production further transform landscapes, often resulting in habitat fragmentation and loss of natural ecosystems.
• Tectonic plate movements
• Volcanic eruptions
• Erosion processes
• Climatic conditions such as temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns
Human activities also have a profound impact on changing geographic landscapes. Urbanization, deforestation, agriculture, industrialization, and mining activities alter the natural terrain and can lead to soil degradation, habitat loss, and changes in biodiversity. Land development for transportation infrastructure, urban sprawl, and energy production further transform landscapes often resulting in habitat fragmentation and loss of natural ecosystems.
The impact of urbanization on land use patterns
Urbanization, characterized by rapid population growth and the expansion of urban areas, has a profound impact on land use patterns. As cities grow and develop, there is an increasing demand for land to accommodate infrastructure, housing, and commercial activities. This often leads to the conversion of agricultural land or natural habitats into built-up areas, resulting in the loss of biodiversity and fragmentation of ecosystems.
The shift in land use from rural to urban areas also has implications for food security and environmental sustainability. With the conversion of agricultural land for urban development, there is a reduction in the availability of land for food production. This can lead to increased reliance on imported food, impacting local economies and contributing to food insecurity. Furthermore, urbanization can result in increased pollution, resource consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating environmental challenges and threatening the long-term health of ecosystems.
• Urbanization leads to the conversion of agricultural land and natural habitats into built-up areas
• Loss of biodiversity and fragmentation of ecosystems are common consequences
• Land use shift from rural to urban areas affects food security and environmental sustainability
• Reduction in land availability for food production can lead to increased reliance on imported food
• Increased pollution, resource consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions are associated with urbanization
Deforestation and its effects on the environment
Deforestation is the clearing of trees and vegetation from forests, resulting in the permanent conversion of land for other purposes such as agriculture, urbanization, and industrial development. The rampant destruction of forests has led to a loss of biodiversity, as many plant and animal species lose their habitats. Additionally, deforestation contributes to climate change by releasing stored carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, further exacerbating global warming.
Moreover, deforestation has adverse effects on the water cycle, as trees play a crucial role in absorbing and releasing water vapor through a process known as transpiration. Without trees, there is an increased risk of soil erosion, flooding, and water pollution. This disruption of the water cycle not only impacts local ecosystems but can also have far-reaching consequences on a global scale, affecting weather patterns and rainfall distribution.
• Deforestation leads to loss of biodiversity as many plant and animal species lose their habitats
• Contributes to climate change by releasing stored carbon dioxide into the atmosphere
• Adverse effects on the water cycle, leading to increased risk of soil erosion, flooding, and water pollution
• Disruption of the water cycle impacts local ecosystems and global weather patterns
The role of agriculture in shaping landscapes
Agriculture plays a significant role in shaping landscapes around the world. Through agricultural practices such as deforestation for arable land, irrigation projects, and the introduction of monoculture crops, vast changes can be observed in the natural environment. The expansion of agricultural areas often leads to the fragmentation of habitats, loss of biodiversity, and soil degradation, altering the landscape’s ecological balance.
Furthermore, the cultivation of certain crops and introduction of pesticides and fertilizers can have detrimental effects on the soil and water quality. Runoff from agricultural fields carrying excess nutrients and chemicals can lead to pollution in water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems and human health. The transformation of landscapes for agricultural purposes not only impacts the environment but also influences the socio-economic dynamics of communities dependent on farming for their livelihoods.
• Agriculture leads to deforestation for arable land
• Irrigation projects alter natural landscapes
• Introduction of monoculture crops changes biodiversity
• Expansion of agricultural areas fragments habitats and causes soil degradation
The cultivation of specific crops and the use of pesticides and fertilizers can have negative impacts on soil and water quality.
– Runoff from fields carrying excess nutrients pollutes water bodies
– Chemicals affect aquatic ecosystems and human health
Transformation of landscapes for agriculture affects not only the environment but also the socio-economic dynamics of farming communities.
Industrialization and its influence on geographic features
Industrialization plays a pivotal role in shaping geographic features as it drives the transformation of natural landscapes into urban areas and industrial zones. The rapid growth of industries leads to an increase in infrastructure development, such as factories, roads, and buildings, altering the topography of the land. This expansion often results in the encroachment of industrial activities into once untouched regions, leading to the degradation of ecosystems and loss of biodiversity.
Moreover, industrialization tends to intensify the demand for natural resources, such as water and minerals, leading to their extraction on a large scale. This extraction process can disturb the natural balance of ecosystems, causing disruption to the hydrological cycle and soil composition. Additionally, the emissions and waste generated by industrial processes can pollute the air, water bodies, and soil, further deteriorating the quality of the environment and impacting the surrounding landscapes.
• Industrialization drives the transformation of natural landscapes into urban areas and industrial zones
• Increase in infrastructure development alters the topography of the land
• Encroachment of industrial activities leads to degradation of ecosystems and loss of biodiversity
• Intensifies demand for natural resources, leading to large-scale extraction
• Extraction process disturbs natural balance of ecosystems, causing disruptions to hydrological cycle and soil composition
• Emissions and waste generated by industrial processes pollute air, water bodies, and soil
The consequences of mining activities on landscapes
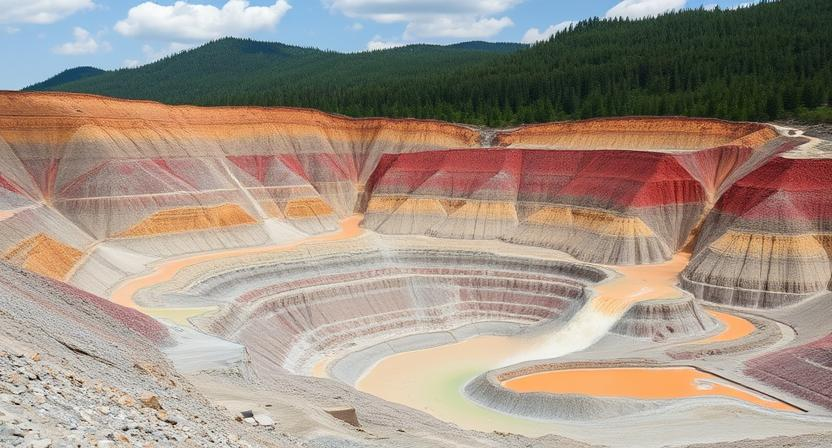

Mining activities can have significant and lasting consequences on landscapes. One of the most apparent impacts is the alteration of land topography, as mining operations often involve excavation and removal of large amounts of earth. This process can result in the destruction of natural landforms and habitats, leading to a loss of biodiversity and disruption of ecosystem functions. Additionally, the creation of mines and associated infrastructure can fragment once continuous landscapes, further exacerbating the ecological impacts of mining activities.
Another consequence of mining on landscapes is the contamination of soil, water, and air with harmful chemicals and heavy metals. The use of explosives, machinery, and chemicals in mining can release toxic substances into the environment, affecting not only the immediate surroundings of the mine but also potentially contaminating larger areas through water and air dispersal. This pollution can have detrimental effects on both human health and the health of ecosystems, causing long-term damage to the land and water resources.
• Alteration of land topography due to excavation and removal of earth
• Destruction of natural landforms and habitats leading to loss of biodiversity
• Fragmentation of once continuous landscapes due to creation of mines and infrastructure
• Contamination of soil, water, and air with harmful chemicals and heavy metals
• Release of toxic substances into the environment through explosives, machinery, and chemicals in mining operations
• Potential contamination of larger areas through water and air dispersal
• Detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems from pollution caused by mining activities
The effects of transportation infrastructure on land development
The presence of transportation infrastructure plays a crucial role in shaping land development patterns. Roads, highways, railways, and airports are key components that influence how and where urban and rural areas expand. Improved connectivity provided by transportation networks often leads to increased real estate development along these corridors. This phenomenon can result in urban sprawl and the conversion of natural landscapes into developed areas.
Moreover, transportation infrastructure can affect land value and land use decisions. Properties located near major transportation hubs or along well-maintained roadways tend to be more desirable for commercial and residential development. As a result, investments in transportation projects can lead to significant changes in land use, potentially causing conflicts between conservation efforts and development goals. The impact of transportation infrastructure on land development underscores the need for careful planning and sustainable practices to balance economic growth with environmental conservation.
• Transportation infrastructure such as roads, highways, railways, and airports shape land development patterns
• Improved connectivity along transportation corridors leads to increased real estate development
• Urban sprawl and conversion of natural landscapes into developed areas can result from transportation infrastructure
• Properties near major transportation hubs or well-maintained roadways are more desirable for development
• Investments in transportation projects can lead to significant changes in land use decisions
• Balancing economic growth with environmental conservation is crucial in planning for the impact of transportation infrastructure on land development.
Urban sprawl and its impact on natural habitats
Urban sprawl, characterized by the rapid expansion of cities into surrounding areas, poses a significant threat to natural habitats. As urban areas grow, they encroach upon previously untouched lands, leading to the fragmentation and destruction of ecosystems. The clearing of forests and wetlands to make way for residential and commercial developments not only displaces wildlife but also disrupts the natural balance of many species, ultimately contributing to a loss of biodiversity.
Moreover, urban sprawl results in increased pollution and habitat degradation, further imperiling the delicate ecosystems that once thrived in these areas. The runoff from roads and buildings carries pollutants into nearby streams and rivers, contaminating water sources and harming aquatic life. The conversion of open spaces into impervious surfaces also exacerbates issues such as flooding and soil erosion, compounding the environmental impacts of urban expansion on natural habitats.
• The fragmentation of habitats due to urban sprawl makes it difficult for wildlife to find suitable areas for feeding, breeding, and migration.
• Increased human-wildlife interactions resulting from encroachment into natural habitats can lead to conflicts and endanger both humans and animals.
• Loss of green spaces in urban areas reduces the availability of essential ecosystem services such as air purification, carbon sequestration, and temperature regulation.
The significance of water management in shaping landscapes
Water management plays a crucial role in shaping landscapes, as it directly impacts the availability and distribution of water resources across regions. Efficient water management practices such as irrigation systems and water conservation techniques can significantly influence the productivity of agricultural lands and the overall vegetation cover in an area. In regions where water scarcity is a pressing issue, strategic water management strategies can help maintain the ecological balance and support sustainable land use practices.
Moreover, effective water management can also contribute to the prevention of soil erosion and the maintenance of ecosystem health. By properly managing water resources, landscapes can be protected from degradation caused by flooding, drought, or excessive water runoff. Implementing watershed management plans and utilizing sustainable water practices not only benefits the environment but also promotes the long-term resilience of landscapes against the impacts of climate change.
• Efficient water management practices such as irrigation systems and water conservation techniques can significantly influence the productivity of agricultural lands
• Strategic water management strategies can help maintain ecological balance in regions facing water scarcity
• Effective water management contributes to prevention of soil erosion and maintenance of ecosystem health
• Properly managing water resources protects landscapes from degradation caused by flooding, drought, or excessive runoff
• Implementing watershed management plans and sustainable water practices promotes long-term resilience against climate change impacts
The relationship between human settlements and geographic features
Human settlements often develop in close proximity to geographic features such as rivers, coastlines, or fertile plains. These features provide essential resources for human survival and have shaped the way communities have evolved over time. For example, settlements near rivers benefit from access to water for drinking, agriculture, and transportation, facilitating trade and economic growth. Coastal areas offer opportunities for fishing and trade, while mountainous regions provide natural defenses and resources like minerals and forests.
Furthermore, the availability of suitable land for agriculture has been a key factor in the establishment and growth of human settlements. Fertile plains and valleys have historically attracted populations due to their capacity to support farming and food production. The geographic features of an area influence the type of land use practices that can be sustained, leading to the development of different settlement patterns based on the resources available. This relationship between human settlements and geographic features highlights the interdependence between communities and the environment in which they reside.
• Settlements near rivers benefit from access to water for drinking, agriculture, and transportation
• Coastal areas offer opportunities for fishing and trade
• Mountainous regions provide natural defenses and resources like minerals and forests
• Availability of suitable land for agriculture has been a key factor in the establishment and growth of human settlements
• Fertile plains and valleys attract populations due to their capacity to support farming and food production
• Geographic features influence the type of land use practices that can be sustained
The effects of climate change on geographic landscapes
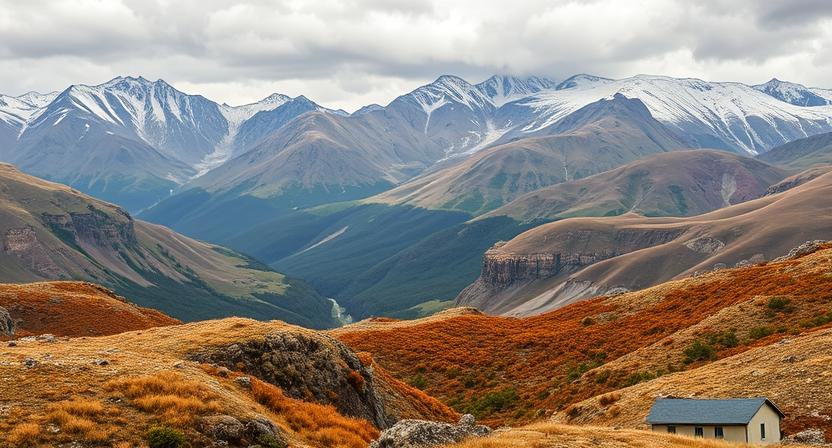

Climate change is significantly impacting geographic landscapes around the world. One of the most prominent effects is the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers, leading to rising sea levels. This phenomenon has the potential to inundate low-lying areas, displacing communities and impacting coastal ecosystems irreversibly. Additionally, altered precipitation patterns due to climate change are causing more frequent and severe droughts in some regions, leading to desertification and soil degradation. These changes in water availability can also affect the biodiversity and productivity of ecosystems, reshaping landscapes in unexpected ways.
• Rising sea levels due to melting polar ice caps and glaciers are inundating low-lying areas
• Displacement of communities and impact on coastal ecosystems
• Altered precipitation patterns leading to more frequent and severe droughts in some regions
• Desertification and soil degradation as a result of changing water availability
• Impact on biodiversity and productivity of ecosystems, reshaping landscapes
The role of tourism in altering natural environments
Tourism has been recognized as a significant industry that can greatly impact natural environments around the world. The influx of tourists to popular destinations often leads to increased stress on the ecosystems and habitats in those areas. Infrastructure development to accommodate visitors, such as hotels, roads, and recreational facilities, can result in habitat destruction, fragmentation, and disruption of wildlife migration patterns. Additionally, the increased waste generation from tourism activities can lead to pollution of water bodies and degradation of landscapes.
Moreover, the sheer volume of foot traffic in ecologically sensitive areas can lead to soil erosion, vegetation loss, and disturbance to fragile ecosystems. Trampling of vegetation, littering, and disturbance of wildlife populations are common issues associated with high tourist activity in natural environments. Furthermore, the demand for souvenirs made from natural resources can drive illegal harvesting of plants and animals, further endangering already vulnerable species and ecosystems.
• Tourism can lead to habitat destruction, fragmentation, and disruption of wildlife migration patterns
• Increased waste generation from tourism activities can result in pollution of water bodies and degradation of landscapes
• Foot traffic in ecologically sensitive areas can cause soil erosion, vegetation loss, and disturbance to fragile ecosystems
• Trampling of vegetation, littering, and disturbance of wildlife populations are common issues associated with high tourist activity
• Demand for souvenirs made from natural resources can drive illegal harvesting of plants and animals
The impact of energy production on land resources
Energy production plays a crucial role in meeting the increasing global demand for power. However, the process of extracting and harnessing energy sources can have significant impacts on land resources. For instance, activities such as mining for coal or drilling for oil can result in deforestation, habitat destruction, and soil degradation. The installation of large-scale energy infrastructure, such as wind farms or solar arrays, also requires extensive land use and can disrupt ecosystems.
In addition to the direct physical footprint of energy production facilities, the transportation and transmission of energy can further impact land resources. The construction of pipelines, power lines, and access roads can fragment habitats, disrupt wildlife corridors, and contribute to soil erosion. Furthermore, the disposal of byproducts and waste materials from energy production processes can pose environmental risks, contaminating soils and water sources. Consideration of these factors is essential in managing the trade-offs between energy development and the conservation of land resources for future generations.
• Mining for coal or drilling for oil can lead to deforestation, habitat destruction, and soil degradation
• Installation of large-scale energy infrastructure like wind farms or solar arrays requires extensive land use
• Transportation and transmission of energy can fragment habitats, disrupt wildlife corridors, and contribute to soil erosion
• Disposal of byproducts and waste materials from energy production processes can contaminate soils and water sources
Waste disposal and its effects on geographic landscapes
Waste disposal practices play a significant role in altering the natural landscape of an area. Improper disposal of waste, whether it is in landfills, incinerators, or dumped illegally, can lead to detrimental effects on the environment. Landfills, for instance, can result in soil contamination and contribute to the release of harmful gases into the atmosphere.
Furthermore, plastic waste, one of the most common forms of solid waste, poses a major threat to ecosystems and landscapes. Plastic products often find their way into water bodies and terrestrial habitats, causing harm to wildlife and disrupting the natural balance of the environment. The accumulation of plastic waste not only degrades the aesthetic appeal of landscapes but also presents long-term environmental challenges that require urgent attention and effective waste management strategies.
• Improper waste disposal can alter natural landscapes
• Landfills can contaminate soil and release harmful gases
• Plastic waste poses a major threat to ecosystems and landscapes
• Plastic products harm wildlife and disrupt the natural balance of the environment
• Accumulation of plastic waste degrades aesthetic appeal of landscapes
The influence of technology on shaping geographic features
Technology plays a pivotal role in shaping geographic features around the world. With advancements in machinery and equipment, humans can now undertake large-scale construction projects that alter the natural landscape. For example, the use of heavy machinery in mining operations can lead to the creation of large open pits and altered topography. Additionally, technologies such as GIS (Geographic Information Systems) enable better mapping and analysis of geographic data, leading to informed decision-making in land use planning and resource management.
Furthermore, the development of technologies like drones and satellite imaging has revolutionized how we study and monitor changes in geographic landscapes. These tools provide high-resolution imagery that allows for detailed analysis of terrain, vegetation cover, and land use patterns. Moreover, remote sensing technologies help track environmental changes over time, such as deforestation rates or urban sprawl expansion. Overall, the influence of technology on shaping geographic features is profound and continues to evolve as new innovations emerge.
• Technology plays a pivotal role in shaping geographic features around the world.
• Advancements in machinery and equipment allow for large-scale construction projects that alter the natural landscape.
• The use of heavy machinery in mining operations can lead to the creation of large open pits and altered topography.
• Technologies like GIS enable better mapping and analysis of geographic data, leading to informed decision-making in land use planning and resource management.
• Drones and satellite imaging revolutionize how we study and monitor changes in geographic landscapes.
• High-resolution imagery from drones and satellites allows for detailed analysis of terrain, vegetation cover, and land use patterns.
• Remote sensing technologies help track environmental changes over time, such as deforestation rates or urban sprawl expansion.
The importance of conservation efforts in preserving landscapes

Conservation efforts play a crucial role in safeguarding the natural beauty and ecological balance of landscapes. By preserving key habitats and biodiversity, conservation helps maintain the delicate interconnections that support various ecosystems. This protection not only benefits wildlife populations but also ensures the sustainability of resources that communities rely on for their well-being.
Furthermore, conservation efforts contribute to the preservation of cultural heritage and historical sites that are integral to our understanding of the past. By safeguarding these landscapes, we can pass down valuable traditions and knowledge to future generations. Conservation also promotes outdoor recreational opportunities that enhance human well-being and foster a deeper connection to nature.
• Conservation efforts help safeguard natural beauty and ecological balance
• Preserving key habitats and biodiversity maintains interconnections in ecosystems
• Benefits wildlife populations and ensures sustainability of resources for communities
• Contributes to preservation of cultural heritage and historical sites
• Passing down valuable traditions and knowledge to future generations
• Promotes outdoor recreational opportunities for human well-being
The effects of war and conflict on geographic environments
War and conflict have profound impacts on geographic environments. The destructive nature of warfare often leads to widespread destruction of land, vegetation, and ecosystems. Aerial bombings, ground combat, and the use of chemical weapons can result in extensive damage to landscapes, altering their natural features and disrupting ecosystems.
Additionally, the presence of military operations in conflict zones can lead to deforestation, soil degradation, and pollution of water sources. The transportation of troops, equipment, and supplies can further disrupt natural habitats and fragment landscapes. Moreover, the aftermath of war often results in the presence of unexploded ordnance and landmines, posing long-term risks to both humans and the environment.
• The destructive nature of warfare often leads to widespread destruction of land, vegetation, and ecosystems
• Aerial bombings, ground combat, and the use of chemical weapons can result in extensive damage to landscapes
• Military operations in conflict zones can lead to deforestation, soil degradation, and pollution of water sources
• Transportation of troops, equipment, and supplies can disrupt natural habitats and fragment landscapes
• Presence of unexploded ordnance and landmines poses long-term risks to both humans and the environment.
The role of government policies in shaping land use
Government policies play a crucial role in influencing how land is used within a country’s borders. These policies dictate what activities can take place in certain areas, such as residential, commercial, industrial, or agricultural use. Through zoning laws, regulations, and incentives, governments can steer development in specific directions to ensure that land is utilized in a way that aligns with their overall goals and objectives.
Furthermore, government policies also play a significant role in promoting sustainable land use practices. By implementing regulations that protect natural habitats, preserve biodiversity, and encourage conservation efforts, governments can help ensure that land is used in a way that minimizes negative impacts on the environment while supporting long-term viability for future generations. In this way, government policies can shape land use in a manner that balances economic development with environmental stewardship.
• Government policies dictate what activities can take place in certain areas
• Zoning laws, regulations, and incentives steer development in specific directions
• Policies promote sustainable land use practices by protecting natural habitats and preserving biodiversity
• Regulations encourage conservation efforts to minimize negative impacts on the environment
• Government policies aim to balance economic development with environmental stewardship for long-term viability.
The impact of globalization on geographic landscapes
Globalization has led to significant changes in geographic landscapes around the world. The increased interconnectedness of economies and cultures has resulted in the expansion of urban areas and the transformation of rural regions into industrial and commercial hubs. This rapid urbanization has often come at the cost of natural habitats and ecosystems, leading to environmental degradation and loss of biodiversity. The pressure to meet global demands for resources and products has driven the exploitation of land and natural resources, further altering the physical and ecological features of landscapes.
Furthermore, globalization has facilitated the spread of technologies and practices that have influenced land use patterns and development. The adoption of modern agricultural techniques, for example, has intensified agricultural activities in many regions, leading to the conversion of forests and grasslands into vast monoculture fields. Additionally, the need for transportation infrastructure to support global trade has resulted in the construction of roads, railways, and ports, which have fragmented landscapes and disrupted natural ecosystems. The globalization of markets and industries has thus played a crucial role in shaping geographic landscapes and posing challenges for sustainable land management practices.
• Globalization has led to the expansion of urban areas and transformation of rural regions into industrial hubs
• Rapid urbanization often comes at the cost of natural habitats and ecosystems
• Pressure to meet global demands drives exploitation of land and natural resources, leading to environmental degradation
• Globalization facilitates spread of technologies influencing land use patterns
• Adoption of modern agricultural techniques intensifies agricultural activities, converting forests into monoculture fields
• Need for transportation infrastructure for global trade leads to landscape fragmentation
Overall, globalization has significantly impacted geographic landscapes by altering physical features, disrupting ecosystems, and posing challenges for sustainable land management practices. As economies become more interconnected, it is crucial to consider the long-term effects on landscapes and prioritize conservation efforts to mitigate environmental degradation.
The significance of indigenous knowledge in sustainable land management
Indigenous knowledge plays a crucial role in sustainable land management. Through generations, indigenous communities have developed valuable practices and techniques that are deeply rooted in their understanding of the land. This traditional knowledge encompasses a wide range of topics such as land conservation, water resource management, and biodiversity preservation. These time-tested practices offer insights into how to maintain the delicate balance between human needs and environmental conservation.
The integration of indigenous knowledge into modern land management strategies can lead to more effective and sustainable outcomes. By recognizing and respecting the wisdom of indigenous communities, we can harness their wealth of experience to inform decision-making processes. This collaborative approach not only promotes environmental sustainability but also supports cultural preservation and fosters mutual respect between different knowledge systems. By incorporating indigenous perspectives into land management practices, we can move towards more holistic and environmentally conscious solutions.
• Indigenous knowledge is deeply rooted in the understanding of the land
• Traditional practices include land conservation, water resource management, and biodiversity preservation
• Time-tested techniques offer insights into maintaining balance between human needs and environmental conservation
• Integration of indigenous knowledge can lead to more effective and sustainable outcomes
• Collaboration promotes environmental sustainability, cultural preservation, and mutual respect between different knowledge systems